

Recent research has identified that significant changes in the Earth’s mantle composition began about 300 million years ago, aligning with the onset of modern plate tectonics and resulting in global chemical heterogeneity.
On present-day Earth, plate subduction continuously modifies the chemical composition of the convecting mantle, and various mantle sources linked to these processes have been studied extensively. However, it remains unclear how Earth’s geodynamic evolution has influenced the convecting mantle’s chemical composition over time and when global chemical heterogeneity of the convecting mantle first emerged in Earth’s geological history.
Now, researchers from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS), along with collaborators from Australia, Switzerland, and the USA, have addressed these questions through a robust compilation of geochemical and isotopic data on intracontinental basaltic rocks over the past billion years.
“This study sheds lights on the long-term cycling of materials within Earth’s interior over geologic time scales,” said Prof. Liu He from IOCAS, the corresponding author of the study.
The study was recently published in Science Advances.
Insights into Mantle Composition Changes
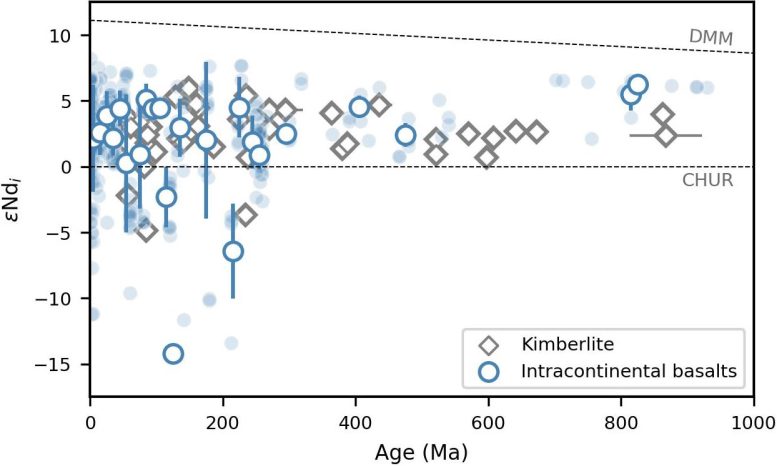
Statistical analysis of the compositions of intracontinental basalts indicates that intracontinental basalts with neodymium (Nd) isotope-enriched geochemical signatures (εNd < 0) occurred only within about the last 300 million years ago (Figure 1). This period coincides with the appearance of kimberlites with signatures of crustal material involvement (Figure 1). These findings suggest a global-scale compositional modification of the convecting mantle.
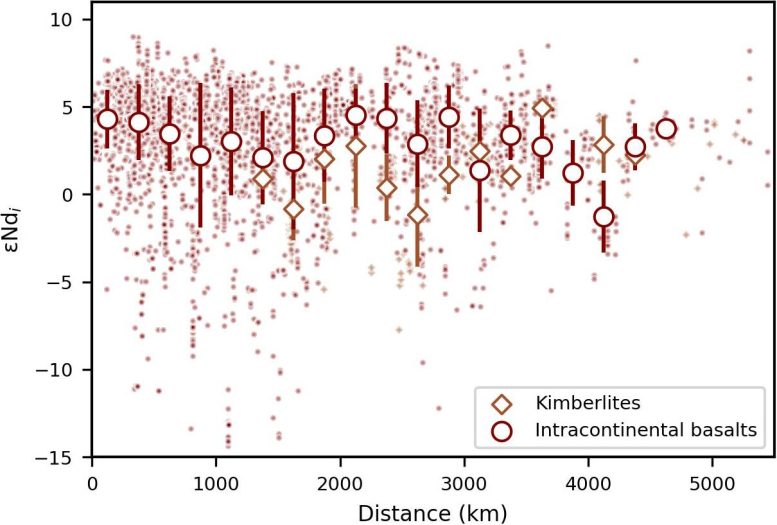
Since the paleogeographic locations of the enriched intracontinental basalts and kimberlites indicate that mantle enrichment was not affected by the distance from subduction zones (Figure 2), the researchers proposed that the enriched signatures in these intracontinental basalts and kimberlites originated from older, more distant subduction events.
Evolution of Plate Tectonics and Mantle Dynamics
Modern-style plate tectonics, marked by continental crust subduction and deep slab break-off, began in the late Neoproterozoic (approx. 700–600 million years ago). Under the modern tectonic regime, widespread cold subduction and continental crust subduction, along with an increased subduction flux during supercontinent assembly (Figure 3), introduced materials from the crust and upper mantle into the lower mantle. After more than 300 million years, these subducted slabs could be transported back to the upper mantle via mantle upwellings.
“This process may have fundamentally altered the composition of the convecting mantle and contributes to the formation of enriched magmas, eventually leading to global-scale chemical heterogeneity of the mantle,” said Dr. Chen Qian from IOCAS, first author of the study.
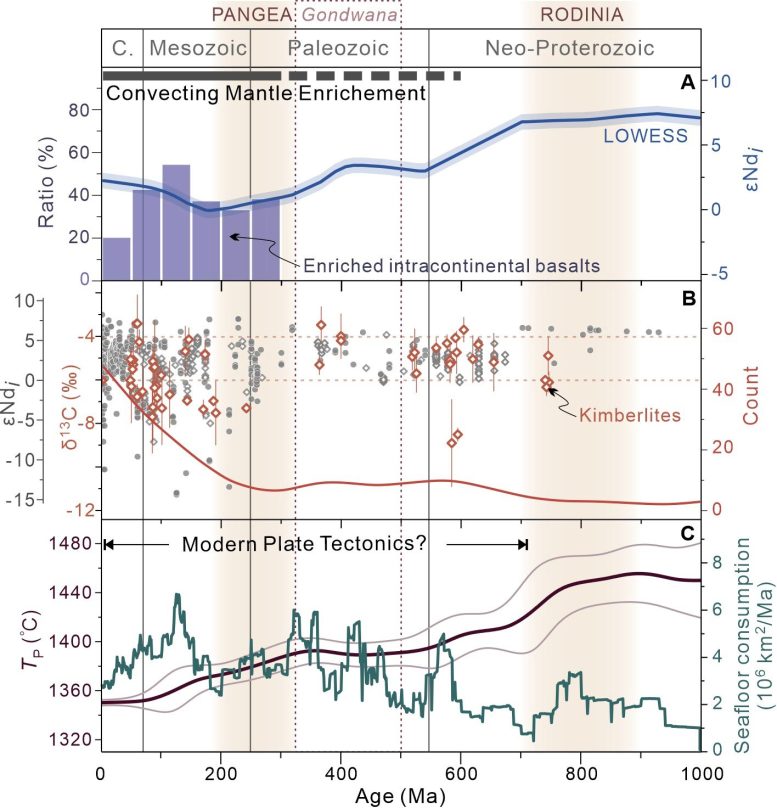
The finding of enriched intraplate mantle-derived magmas appearing approx. 300 million years after the onset of modern plate tectonics provides important insights into the processes, driven by plate tectonics, that are involved in the compositional diversity of Earth’s convecting mantle, according to the researchers.
“The time frame aligns with models suggesting that it takes considerable time for subducted materials to affect the composition of the upper mantle through these dynamic processes,” said Prof. Liu.
Reference: “Global mantle perturbations following the onset of modern plate tectonics” by Qian Chen, He Liu, Andrea Giuliani, Luc S. Doucet, Tim E. Johnson, Lipeng Zhang and Weidong Sun, 16 October 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq7476