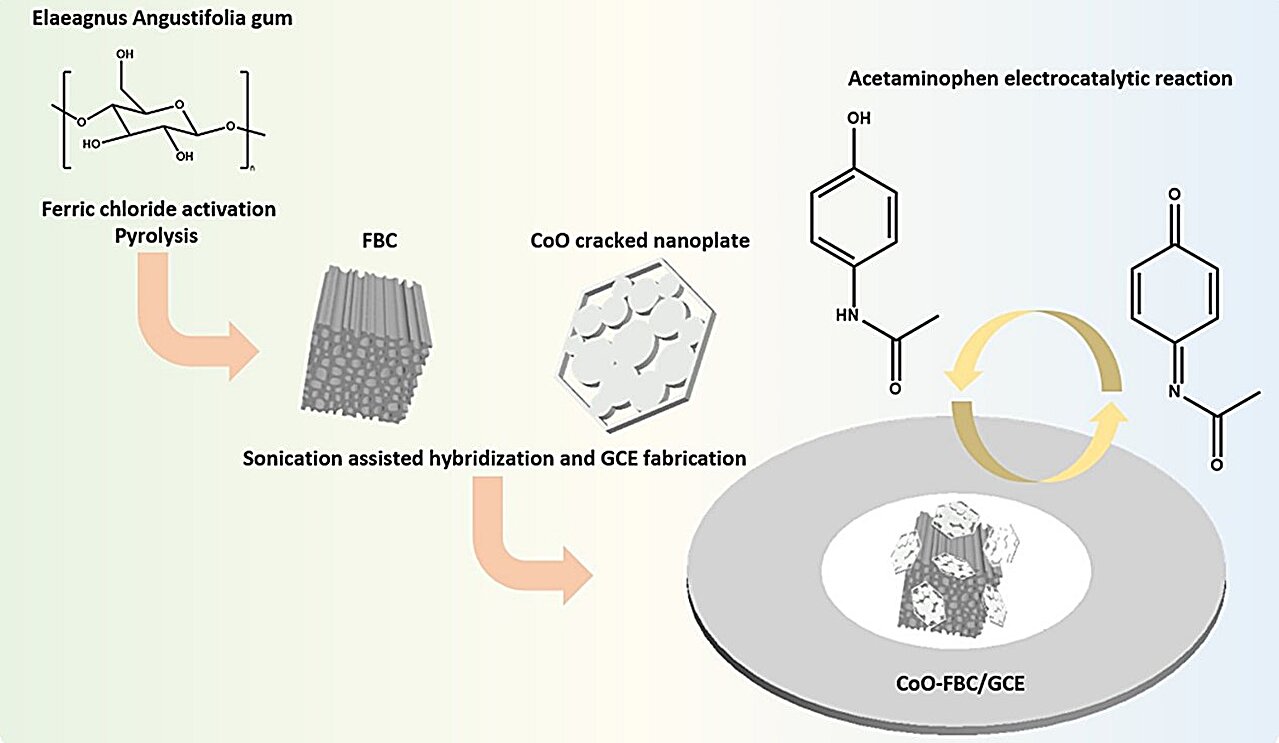
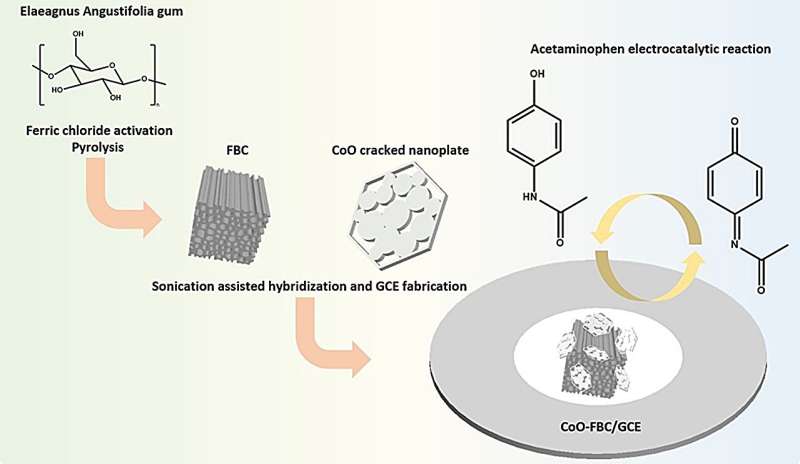
In recent years, the excessive use of acetaminophen (APAP) has become a significant human hazard and social burden. Rapid and automated electrochemical detection has emerged as a crucial method for measuring APAP concentration in human urine.
A recent study explores a novel porous cobalt-derived biomass electrocatalyst material prepared from Elaeagnus angustifolia gum and investigates its electrochemical properties as well as its specific detection capability for APAP. The work is published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials on 18 July 2024.
Acetaminophen (APAP) is a commonly used analgesic and antipyretic drug. Due to misuse, there is an excessive presence of APAP in bodily fluids, leading to significant side effects such as acute liver injury and liver failure. Currently, the methods for detecting APAP in the human body are relatively expensive and complex.
Using natural Elaeagnus angustifolia gum as the base material, a series of treatments including high-temperature calcination are conducted. This material is then activated with ferric chloride to produce a porous natural carbon-based material with a significantly increased specific surface area, which is 2.6 times that of BC.
Based on relevant research, cobalt oxide doping was chosen to enhance conductivity, enabling specific recognition of APAP molecules in urine during selective and sensitive testing for acetaminophen detection. The Ipa of FBC-CoO/GCE modified with cobalt oxide is nearly twice that of FBC/GCE. Compared to traditional liquid chromatography detection methods, it offers faster speed, higher sensitivity, miniaturization, and automation.
This study employed natural resources like Elaeagnus angustifolia gum to produce FBC via straightforward preparation steps. By modifying the preparation process, we adjusted the hollowness of cobalt oxide cracked nanosheets, thereby synthesizing APAP sensors with excellent sensitivity. In this study, the uric acid and APAP reaction peaks can be effectively separated and identified within a reasonable physiological concentration range.
Further enhancements can elevate the performance of CoO-FBC/GCE, setting the stage for in-depth research in upcoming projects. These enhancements encompass exploring the biomass activation process, tailoring the size and morphology of cobalt oxide cracked nanosheets, examining the ultrasonic steps and the ratio between biomass carbon and cobalt oxide, refining the alkaline co-precipitation method, and co-doping with other transition elements, all aimed at achieving high-performance sensors.
The research team includes Yihan Zhang, Zehong Gao, Xamxikamar Mamat and Longyi Chen from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences; and Yiliyasi Baikeli from College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Dezhou University.
More information:
Yihan Zhang et al, Improved voltammetric discrimination of acetaminophen and uric acid in urine using CoO biochar nanocomposite, Industrial Chemistry & Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4IM00069B
Provided by
Industrial Chemistry & Materials
Citation:
Biochar nanocomposite enhances detection of acetaminophen and uric acid in urine (2024, October 16)
retrieved 16 October 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-10-biochar-nanocomposite-acetaminophen-uric-acid.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.