

Research highlights how the meteor impact that ended the dinosaurs helped spawn the mutualistic relationship between ants and fungi, marking an early form of agriculture long before humans farmed.
The meteor strike that killed the dinosaurs 66 million years ago may have led to a remarkable mutually beneficial relationship between fungi and ants. The low-light environment caused by the impact created conditions favorable to the spread of fungi that feed on organic matter, which was abundant at the time as plants and animals were dying in droves.
According to a new study published in Science, this was the perfect opportunity for the ancestor of a group of ants to start cultivating these microorganisms.

Fungal Strains and Genetic Insights
“The origin of fungus-farming ants was relatively well understood, but a more precise timeline for these microorganisms was lacking. The work provides the smallest margin of error to date for the emergence of these fungal strains, which were previously thought to be more recent,” explains André Rodrigues, professor at the Institute of Biosciences of São Paulo State University (IB-UNESP) in Rio Claro, Brazil, and one of the authors of the paper.
The researcher coordinates the project “Collaborative research: Dimensions US-São Paulo: integrating phylogeny, genetics, and chemical ecology to unravel the tangled bank of the multipartite fungus-farming ant symbiosis,” supported by FAPESP through its Research Program on Biodiversity Characterization, Conservation, Restoration and Sustainable Use (BIOTA), in collaboration with the National Science Foundation (NSF), of the United States.

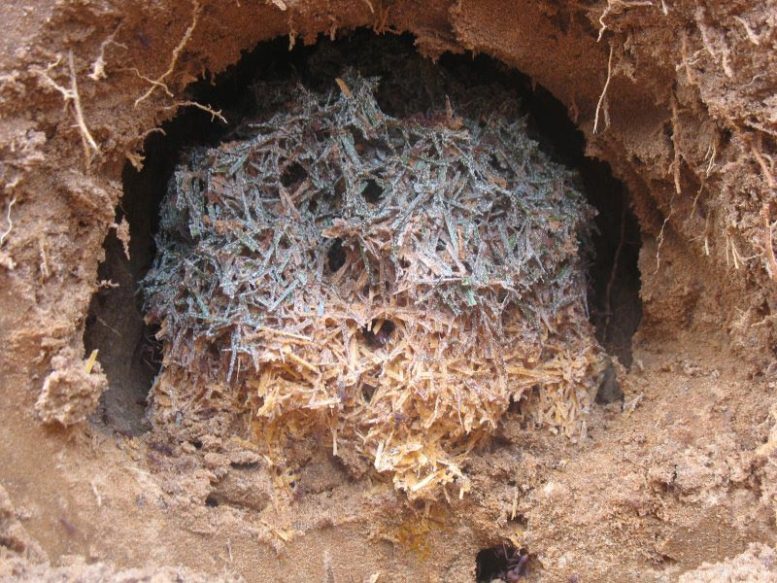
The dating was made possible by analyzing the so-called ultraconserved elements (UCEs) of the genomes of 475 fungal species cultivated by ants and collected from different parts of the Americas. UCEs are regions that remain in the genome throughout the evolution of a group, derived from its most ancient ancestors.
“In this case, we were interested in the regions close to these elements. They show the most recent differences between species and allow us to trace a fairly accurate evolutionary line,” adds Pepijn Wilhelmus Kooij, a researcher at IB-UNESP supported by FAPESP and also co-author of the work.
Using this method, it was possible to establish the near-simultaneous emergence of two distinct fungal lineages from the same ancestor of today’s leafcutter ants (a group known as Attini) 66 million years ago.
Mutualism and Agricultural Origins
Specialists in the mutualism between fungi and ants have long argued that the beginning of this relationship defines the emergence of agriculture, tens of millions of years before humans began domesticating plants, just 12,000 years ago.
The study also revealed the emergence of an ancestor of coral fungi, a second group that began to be cultivated by ants 21 million years ago. The fungus gets its name from the fact that it forms structures that resemble miniature colonies of sea coral.
Nutritional Mutualism and Fungal Adaptation
The results support the hypothesis that fungi had already undergone pre-adaptation before being cultivated by ants. It is likely, the authors point out, that the ancestor of the leafcutter ant group lived near fungi, either inside the colonies or even collecting them from time to time to feed on them or their products.
“But the fungi were not an essential part of the ants’ diet. The pressure exerted by the meteor impact may have turned this relationship into an obligatory mutualism, in which these fungi come to depend on the ants for food and reproduction, while at the same time the ants depend exclusively on the fungi as a food source,” Rodrigues contextualizes.
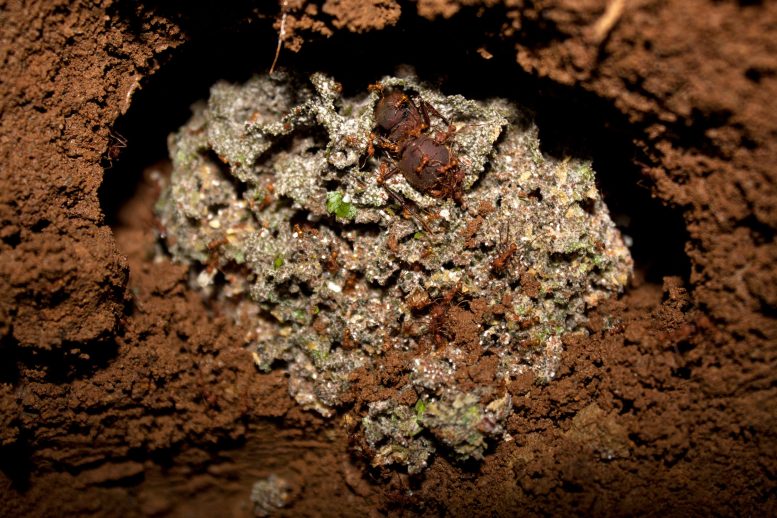
Today, four different groups of ants cultivate four types of fungus. In some cases, the insects even alter the growth of the cultivated product so that it provides certain nutrients.

“When we cultivate them in the lab, the fungi take the expected form of hyphae. However, inside the colony, one of these hyphae types becomes swollen and forms structures similar to grape clusters, rich in sugars. We still don’t know how the ants do this,” says Kooij.
For Mauricio Bacci Junior, professor at IB-UNESP and co-author of the paper, the origin of the cultivation of fungi probably points to an adaptation in the face of a nutritional shortage faced by the ants at that time.
With the abundance of fungi spreading across what are now the Americas, and fewer options for food sources, those that already had some possible relationship with ants ended up proving more useful when cultivated.
“To feed itself, the fungus decomposes the organic matter carried by the ants. In turn, the ant consumes substances produced by the fungus that it couldn’t obtain from any other source. It’s as if the fungus were the insect’s external stomach,” compares the researcher, who is deputy director of the Center for Research on Biodiversity Dynamics and Climate Change (CBioClima), one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDCs) supported by FAPESP.
Agricultural Evolution and Biotechnological Potential
After this founding event, fungus-farming ants, which had previously lived in humid forests, experienced a second selective pressure with the expansion of the Cerrado savanna-like biome 27 million years ago. With more open and arid areas, there was a diversification of these agricultural insects, leading to the origin of today’s leafcutter ants.
This event also certainly favored the diversification of fungi, which became more efficient at producing food for the ants and decomposing organic matter.
So much so that the enzymes produced by fungi cultivated by ants are now being studied for their biotechnological potential to degrade not only organic matter but also other materials, including plastics.
Reference: “The coevolution of fungus-ant agriculture” by Ted R. Schultz, Jeffrey Sosa-Calvo, Matthew P. Kweskin, Michael W. Lloyd, Bryn Dentinger, Pepijn W. Kooij, Else C. Vellinga, Stephen A. Rehner, Andre Rodrigues, Quimi V. Montoya, Hermógenes Fernández-Marín, Ana Ješovnik, Tuula Niskanen, Kare Liimatainen, Caio A. Leal-Dutra, Scott E. Solomon, Nicole M. Gerardo, Cameron R. Currie, Mauricio BacciJr., Heraldo L. Vasconcelos, Christian Rabeling, Brant C. Faircloth and Vinson P. Doyle, 3 October 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adn7179