

Researchers have uncovered the genetic basis of anthocyanin regulation in mulberries, identifying key genes that could help improve fruit color, nutritional value, and market appeal.
A recent study has uncovered the genetic mechanisms behind anthocyanin content in mulberries, shedding light on the factors that control fruit color and nutritional value. By sequencing and comparing the genomes of two different mulberry cultivars, researchers identified crucial genetic variations and highlighted the significant role of MaVHAG3 in anthocyanin production. These findings provide a valuable biotechnological framework for improving mulberry fruit traits.
Mulberry fruits are celebrated for their vibrant colors, nutritional value, and potential health benefits. Anthocyanins, the primary pigments in purple mulberries, are known for their antioxidant properties and role in human health. However, understanding the genetic basis of anthocyanin regulation in mulberry fruits has been challenging due to their complex genomes. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need for in-depth research to better understand and manipulate mulberry fruit pigmentation.
Genome Analysis of Mulberry Cultivars
On April 23, 2024, researchers from Southwest University in Chongqing, China, published a pivotal study in Horticulture Research. The team generated haplotype-resolved genome assemblies for two mulberry cultivars, ‘Zhongsang5801’ (high anthocyanin) and ‘Zhenzhubai’ (low anthocyanin). Their comprehensive analysis identified key genes and regulatory mechanisms underlying anthocyanin content in mulberries, paving the way for genetic enhancement of mulberry cultivars.
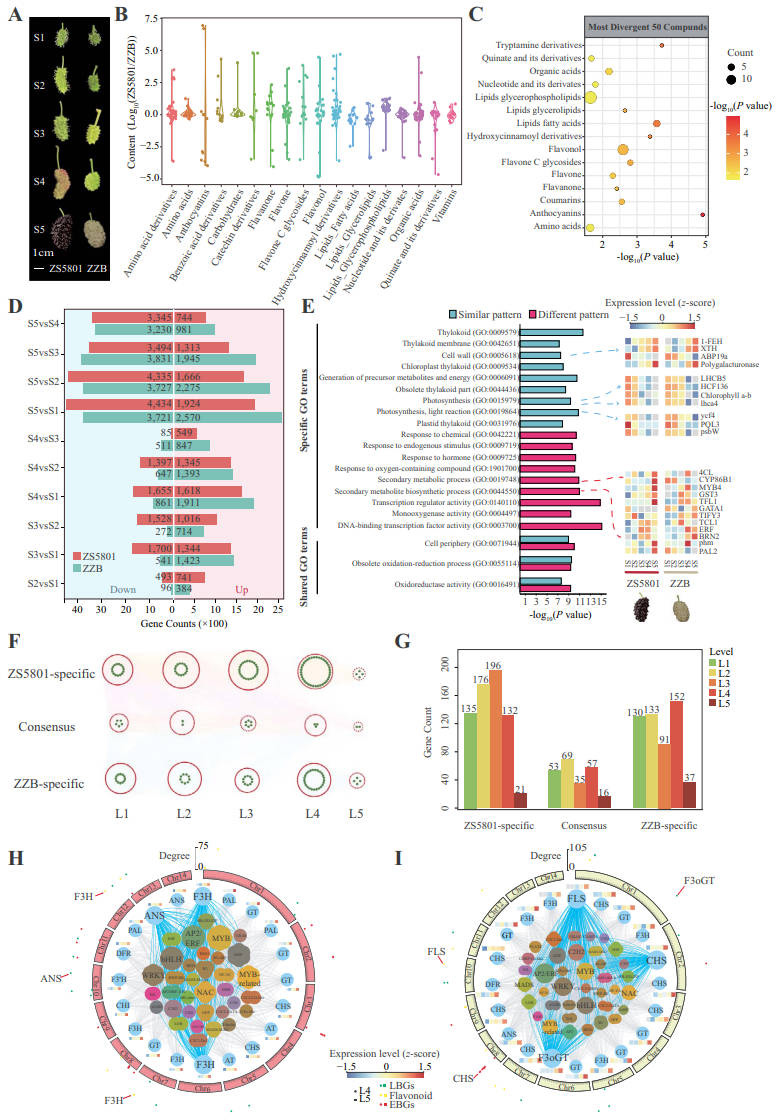
The study involved sequencing the genomes of ‘Zhongsang5801’ (ZS5801) and ‘Zhenzhubai’ (ZZB), followed by a detailed comparative analysis of their genomic and transcriptomic data. The researchers identified MaVHAG3, a vacuolar-type H+-ATPase G3 subunit gene, as crucial in anthocyanin accumulation. By comparing gene expression across developmental stages, they found that ZS5801 exhibited significantly higher levels of anthocyanins and flavonoids compared to ZZB. The analysis also revealed expansions and contractions in flavonol synthase (FLS) and dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) genes, which impact carbon flow in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathways. These findings highlight the intricate genetic and molecular processes that regulate fruit coloration in mulberries.
Dr. Aichun Zhao, the corresponding author, commented, “Our research provides a comprehensive understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms controlling anthocyanin content in mulberries. These insights are critical for developing new cultivars with enhanced nutritional and aesthetic qualities. The high-quality genome assemblies we generated will serve as a valuable resource for future research and breeding programs.”
The findings from this study have significant implications for the agricultural and food industries. By understanding the genetic basis of anthocyanin regulation, breeders can develop mulberry cultivars with higher anthocyanin content, leading to fruits with better nutritional profiles and health benefits. Additionally, the enhanced pigmentation traits can improve the market appeal of mulberry products. This research also sets the stage for further studies on other fruit crops, potentially leading to broader applications in horticulture and biotechnology.
Reference: “Haplotype-resolved chromosomal-level genome assembly reveals regulatory variations in mulberry fruit anthocyanin content” by Zhongqiang Xia, Wei Fan, Duanyang Liu, Yuane Chen, Jing Lv, Mengxia Xu, Meirong Zhang, Zuzhao Ren, Xuefei Chen, Xiujuan Wang, Liang Li, Panpan Zhu, Changying Liu, Zhiguang Song, Chuanshu Huang, Xiling Wang, Shuchang Wang and Aichun Zhao, 23 April 2024, Horticulture Research.
DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae120