

Johns Hopkins researchers reactivated a memory circuit in mice, causing them to seek shelter even when no threat or shelter was present. The findings could lead to novel approaches for researching and treating memory loss in humans, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Using a sophisticated brain-imaging system, neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have successfully reactivated a specific memory circuit in mice, causing them to seek out shelter when no shelter is actually present.
The researchers say the study, published Sept. 27 in Nature Neuroscience, advances understanding of how memories are structured in the mammalian brain. The findings could one-day point to new ways of slowing down or preventing the memory loss that accompanies Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Specifically, the team found that stimulating neurons in two areas of mouse brains — the nucleus accumbens, also known as the brain’s “pleasure center” responsible for relaying dopamine-dependent behaviors, and the dorsal periaqueductal gray (dPAG), responsible for defensive behavior — reactivated a “spatial memory” and caused the mice to seek shelter.
“When we artificially reactivate those memory circuits in the brain, it triggers the mouse to do the same thing it did naturally, even without the fear stimuli that cause them to seek shelter to begin with,” says senior author Hyungbae Kwon, Ph.D., associate professor of neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Mapping Brain Functions Related to Spatial Memory
The scientists say they aimed to map out which areas of the brain are responsible for navigating one’s surroundings, a high-level cognitive function among mammals, including humans. Thus, these experiments, which tested whether such cognitive brain functions can be replayed randomly, may have applications in understanding how other mammals behave, perceive, and sense their environment.
In the new experiments, the researchers first allowed laboratory mice to explore their surroundings in a box with a shelter in the corner. The team placed a series of visual cues, including triangles, circles, and stripes in different colors, to help the mice locate the shelter based on nearby landmarks. The mice acclimated to the area for seven minutes, entering and exiting the shelter.
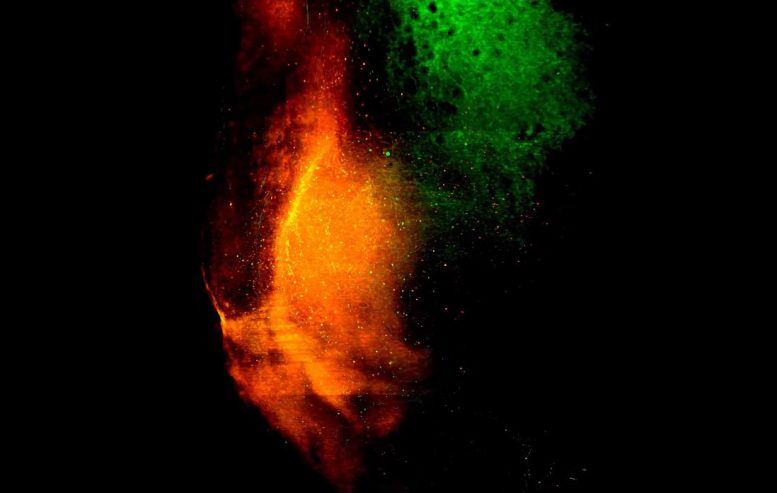
Then, the researchers added a visual or auditory looming signal to spur them to seek shelter – also forming a spatial memory relative to their location and the visual cues.
To selectively tag shelter memory neurons, the researchers used a light-activated gene-expression switching system called Cal-light, which Kwon developed in 2017. Once the scientists identified these neurons in the nucleus accumbens, they switched on expression of the genes associated with them, reactivating the shelter-seeking memory in mice while also activating neurons in the dPAG.
In turn, the mice sought out the area of the box where the shelter had once been, when neither the original threat nor the shelter were present.
To get to this point, the researchers first selectively activated neurons in the nucleus accumbens and then, separately, in the dPAG, to see whether switching on neurons in just one area of the brain would cause this behavior.
Insights into Memory and Future Applications
“Surprisingly, we found that the mice did not seek out shelter when we activated neurons in the nucleus accumbens alone,” Kwon says. “Whereas switching on neurons in the dPAG caused the mice to react randomly, but did not guide them specifically to the area where they sought shelter before.”
“The Cal-light system allowed us to selectively tag a specific function in the brain, helping us to map out memory on a cellular level,” says Kwon.
Eventually, Kwon says this research could provide a foundation for reactivating or engineering memory circuits in people with Alzheimer’s.
“If we understand the macro-level structure of memory, then we may be able to develop more effective strategies to prevent or slow down neurodegenerative diseases using this method,” he says.
The researchers say they hope to understand brain-wide memory structure by selectively tagging and reactivating neurons with different functions in different areas of the brain that lead to other specific behaviors.
“Understanding how all of these memory circuits work together will help us understand brain function better,” he says.
Reference: “Dopamine-mediated formation of a memory module in the nucleus accumbens for goal-directed navigation” by Kanghoon Jung, Sarah Krüssel, Sooyeon Yoo, Myungmo An, Benjamin Burke, Nicholas Schappaugh, Youngjin Choi, Zirong Gu, Seth Blackshaw, Rui M. Costa and Hyung-Bae Kwon, 27 September 2024, Nature Neuroscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01770-9
Other researchers involved in the study are Kanghoon Jung, Sarah Krüssel, Sooyeon Yoo, Benjamin Burke, Nicholas Schappaugh, Youngjin Choi and Seth Blackshaw of Johns Hopkins; Myungmo An of the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience; and Zirong Gu and Rui M. Costa of the Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute at Columbia University and the Allen Institute.
Funding for this work was provided by the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, a National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression Young Investigator Grant and National Institutes of Health Grants R01MH107460, 5U19NS104649, K99 NS119788, DK108230 and DP1MH119428.