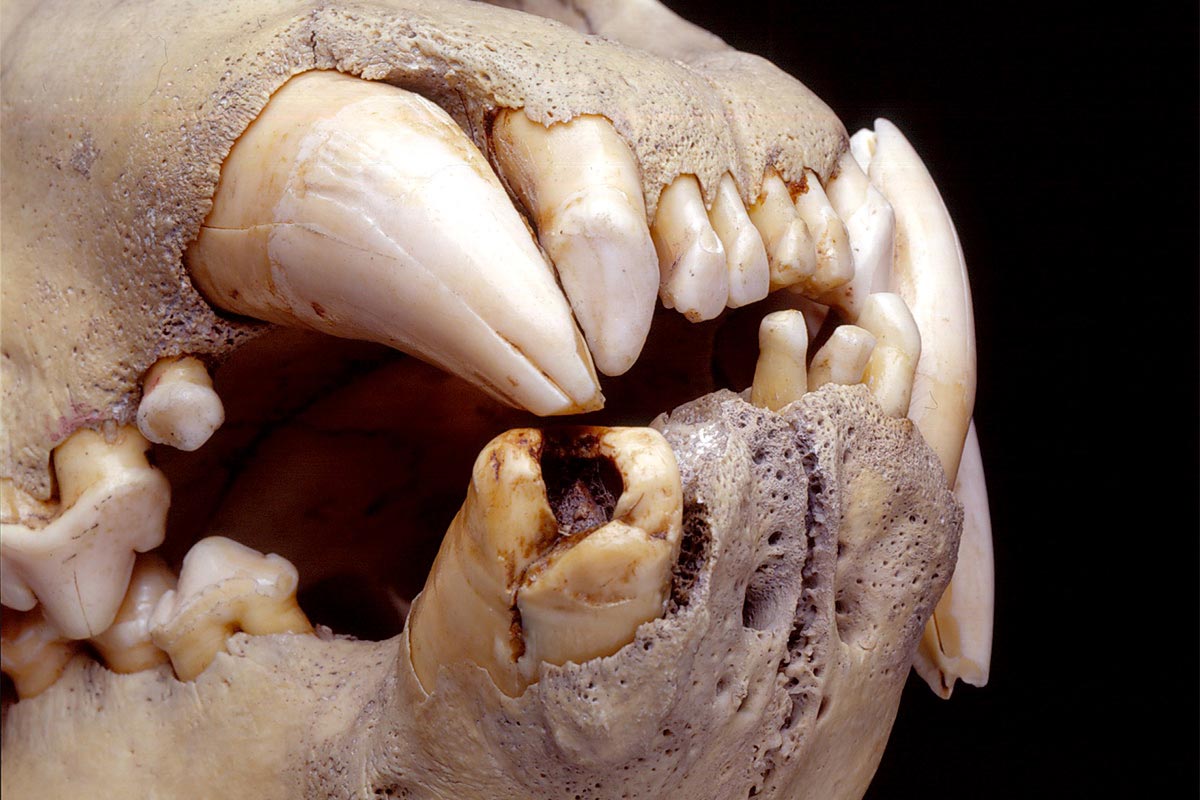
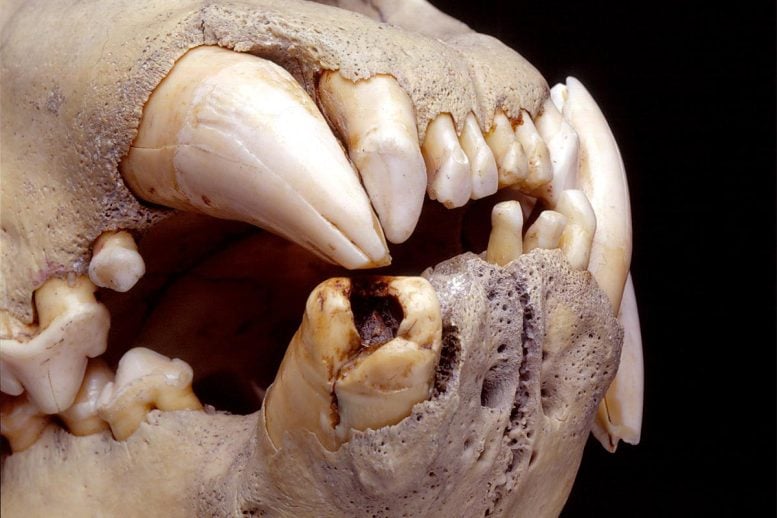
Research on Tsavo lion museum specimens from the 1890s, using DNA isolated from hairs in their teeth, reveals a diverse diet including humans, giraffes, and wildebeests.
This study, facilitated by advanced biotechnologies, sheds light on the historical ecology of these notorious man-eaters and the environmental impacts of colonization in Kenya.
Discovering the Diet of Historical Tsavo Lions
By isolating and analyzing DNA extracted from compacted hairs found in the teeth of two Tsavo lion museum specimens from the 1890s, researchers have discovered that these historic lions from Kenya preyed on a variety of species, including humans, giraffes, and wildebeests. Known as the “Tsavo Man-Eaters,” these lions are believed to have killed at least dozens of people, many of whom were working on the Kenya-Uganda Railway in the late 1890s. The findings were published today (October 11) in the journal Current Biology.
“As biotechnologies advance, there are unexpected sources of knowledge, in this case genomics, that can be used to inform about the past,” says Ripan Malhi of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. “Our results inform on the ecology and diet of lions in the past as well as on the impacts of colonization on life and land in this region of Africa.”
Innovating Historical DNA Analysis Techniques
“A key part of this study was to create a method to extract and analyze DNA from single hairs of prey species found in the teeth of historical museum specimens,” says Alida de Flamingh, also at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. “Our analysis showed that the historic Tsavo lions preyed on giraffe, human, oryx, waterbuck, wildebeest, and zebra, and we also identified hairs that originated from lions. This method can be used in many ways, and we hope other researchers will apply it to study prey DNA from other animal skulls and teeth.”

Implications and Future Prospects of Prey DNA Analysis
Study co-author Tom Gnoske at the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago was the first to consider reconstructing the diet of these historic lions using prey hairs from their skulls, the researchers say. With collaborators in Kenya, he began to identify the hairs using microscopy. While conducting ancient DNA research on other animals at the Field Museum, the University of Illinois team got the idea to add genomics as a complementary approach to the study of those compacted hairs.
The Tsavo lions in the new study had dental injuries, including partially broken canine teeth exposing cavities where hair from their prey built up over time. From those tooth cavities, the researchers extracted DNA from individual hair shafts and tiny clumps of hair fragments. While the DNA in those samples was degraded in ways that are typical for historic or ancient DNA, they were able to piece enough of it back together in some of the samples to identify the species the hair originated from. They ultimately identified six prey species, including giraffe, human, oryx, waterbuck, wildebeest, and zebra.

The DNA data narrowed the giraffe sample down to a subspecies of Masai giraffe from southeast Kenya. The researchers also found Tsavo lion DNA that most closely matched other East African lions from Kenya and Tanzania. The researchers said they were most surprised to find hair from wildebeest, noting that it raises questions about their distribution in the past.
“It suggests that the Tsavo lions may have either traveled farther than previously believed, or that wildebeest were present in the Tsavo region during that time,” de Flamingh said. “The closest grazing area for wildebeest was over 50 miles from where the lions were killed in 1898 at the Tsavo-Athi confluence.”
The researchers say they are excited to explore the findings in even greater detail. For example, they suggest that the layered hairs can allow them to go back in time to reconstruct the lions’ diet at different ages. They suggest that such analysis may offer insight into human-lion conflicts that continue to impact communities in Africa, where lions may prey on wildlife as well as domestic animals and humans. The method also holds promise for studies of even older specimens.
“This methodology can potentially be used on hairs from broken teeth of more ancient carnivores from hundreds to thousands of years ago,” Malhi said. “The method opens up a new avenue of inquiry into the past.”
Reference: “Compacted hair in broken teeth reveal dietary prey of historic lions” 11 October 2024, Current Biology.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.09.029
This work was supported by the US Department of Agriculture, USAID, and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.