Recently, a research team led by Professor Wu Yuejin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, discovered a key gene that can influence rice grain length by regulating cell proliferation, the RGL2 gene. This provides new genetic resources for high-yield breeding of rice. The related findings were recently published in Physiologia Plantarum.
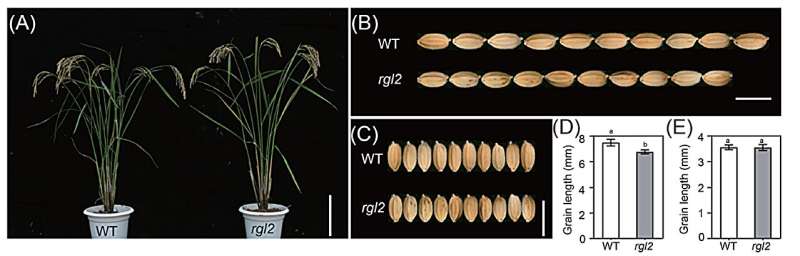
High yield is one of the primary objectives in rice breeding, and grain type like grain length and width is an important agronomic trait affecting yield. Wu’s team obtained this rgl2 mutant in their research, which exhibited shorter grain length without changes in grain width through physical mutagenesis.
Cytological analysis revealed that the reduction in grain length was primarily due to a decrease in cell number rather than changes in cell length. Mapping and functional analysis indicated that RGL2 encoded a keratin-associated protein (KAP), which was expressed at a higher level in the young panicle. Overexpression of RGL2 significantly increased grain length and enhanced single-plant yield by promoting cell proliferation in the grain.
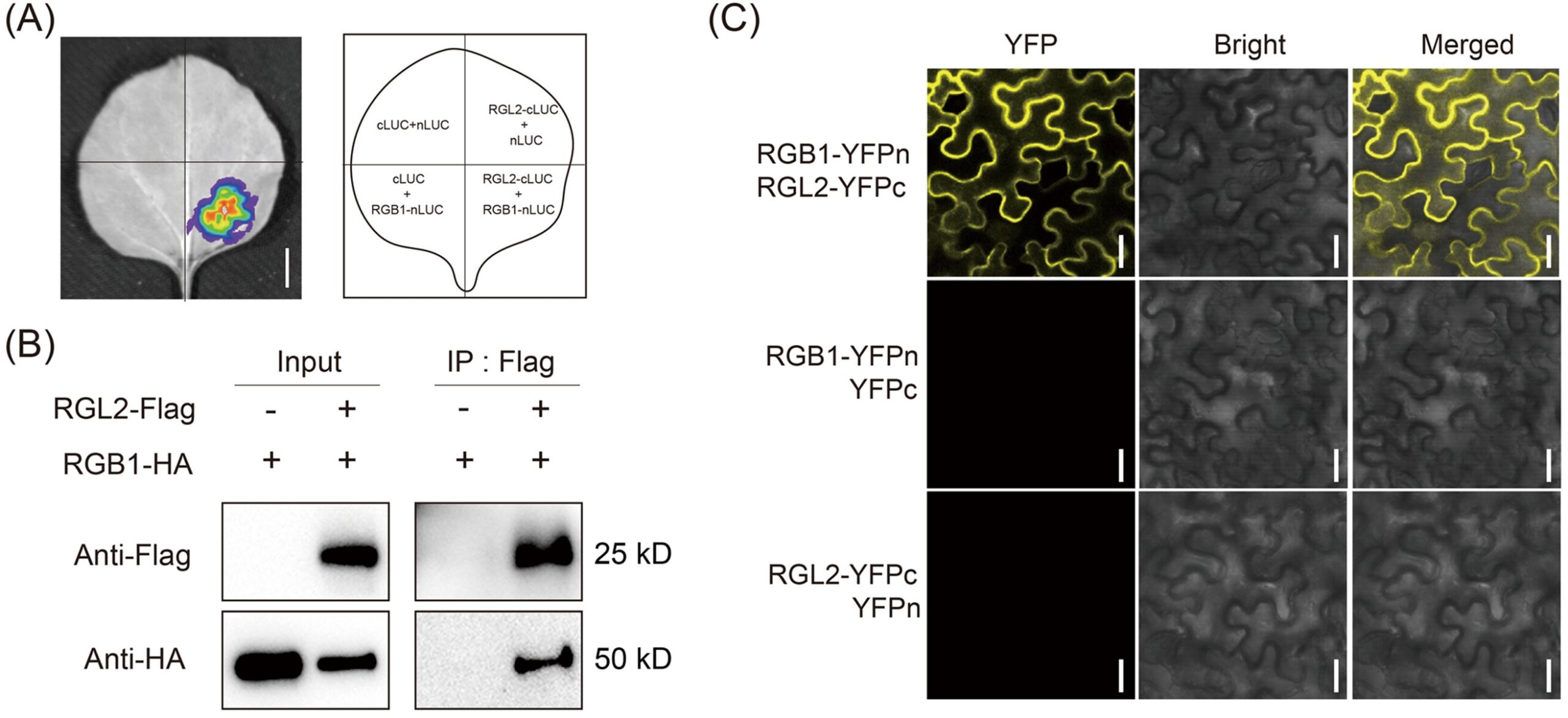
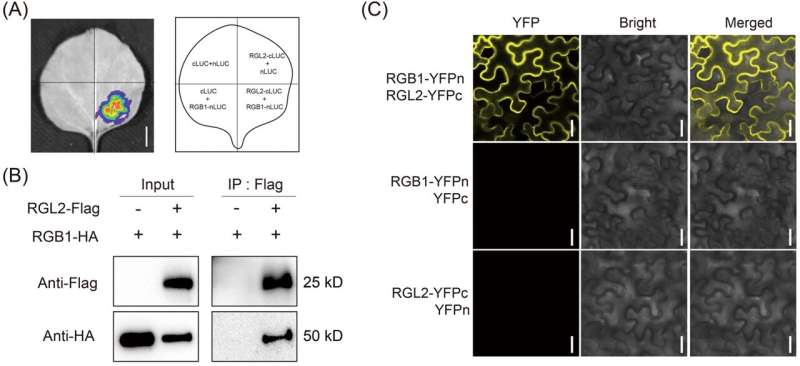
Additionally, OsRGL2 interacted with the RGB1 protein, suggesting that it may positively regulate grain type and yield through the G protein signaling pathway.
The researchers also found that RGL2 might affect grain length by regulating the cell cycle. In simple terms, RGL2 helped rice grains grow longer by regulating genes related to cell cycle and promoting the growth of more cells.
This discovery not only deepens our understanding of the genetic mechanisms of rice grain type, but also provides new strategies and directions for molecular design breeding aimed at high rice yield.
More information:
Chunpeng Chen et al, Mutation of KAP, which encodes a keratin‐associated protein, affects grain size and yield production in rice, Physiologia Plantarum (2024). DOI: 10.1111/ppl.14528
Provided by
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Citation:
Key gene discovered for regulating rice grain length (2024, October 10)
retrieved 10 October 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-10-key-gene-rice-grain-length.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.