

NASA engineers have deactivated the plasma science instrument on the Voyager 2 spacecraft as its power diminishes over time.
Despite this, the spacecraft, which is over 12.8 billion miles from Earth, continues to conduct research with its remaining four instruments. This effort to conserve power aims to extend its operational capability into the 2030s, a testament to its unique role in exploring the interstellar space beyond our solar system.
Power Management on Voyager 2
NASA mission engineers have turned off the plasma science instrument aboard the Voyager 2 spacecraft due to the probe’s gradually diminishing electrical power supply.
While it continues traveling more than 12.8 billion miles (20.5 billion kilometers) from Earth, the spacecraft is still operating four science instruments to study the region outside our heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields created by the Sun. The probe has enough power to continue exploring this region with at least one operational science instrument into the 2030s.

Unprecedented Mission Challenges
Mission engineers have taken steps to avoid turning off a science instrument for as long as possible because the science data collected by the twin Voyager probes is unique. No other human-made spacecraft has operated in interstellar space, the region outside the heliosphere.
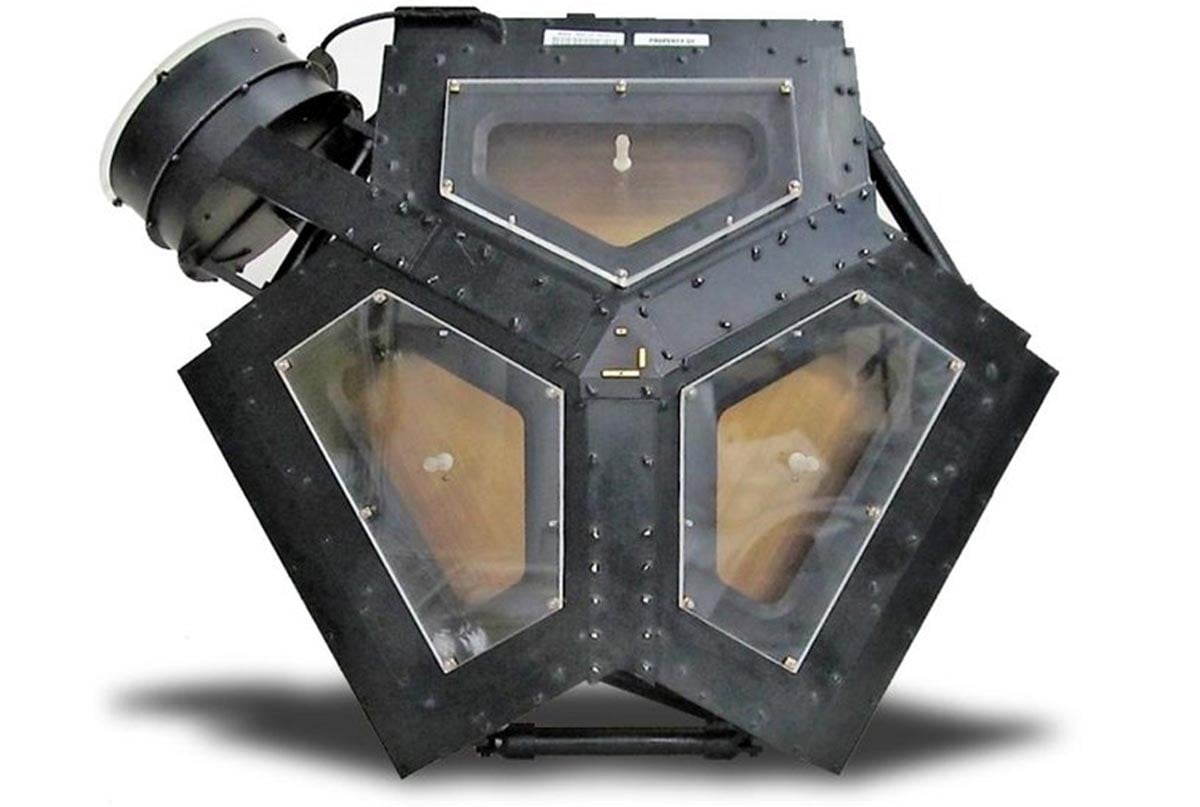
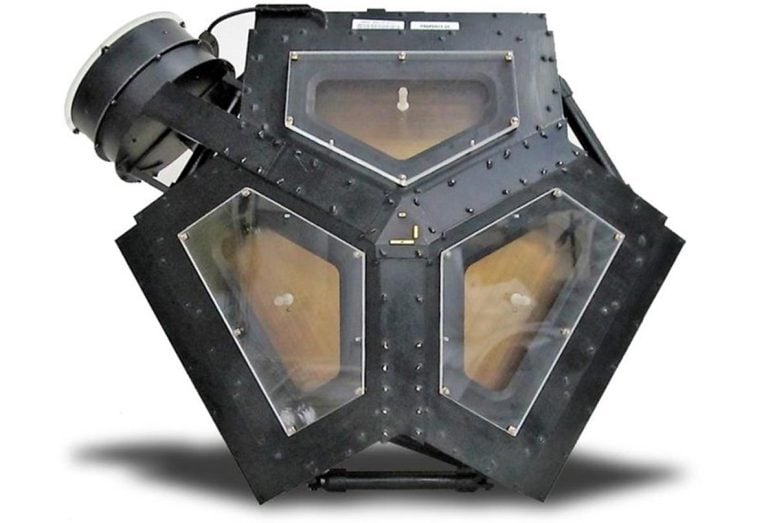
The plasma science instrument measures the amount of plasma (electrically charged atoms) and the direction it is flowing. It has collected limited data in recent years due to its orientation relative to the direction that plasma is flowing in interstellar space.

Strategies for Power Conservation
Both spacecraft are powered by decaying plutonium and lose about 4 watts of power each year. After the twin Voyagers completed their exploration of the giant planets in the 1980s, the mission team turned off several science instruments that would not be used in the study of interstellar space. That gave the spacecraft plenty of extra power until a few years ago. Since then, the team has turned off all onboard systems not essential for keeping the probes working, including some heaters. In order to postpone having to shut off another science instrument, they also adjusted how Voyager 2’ voltage is monitored.
Monitoring Results
On September 26, engineers issued the command to turn off the plasma science instrument. Sent by NASA’s Deep Space Network, it took 19 hours to reach Voyager 2, and the return signal took another 19 hours to reach Earth.
Mission engineers always carefully monitor changes being made to the 47-year-old spacecraft’s operations to ensure they don’t generate any unwanted secondary effects. The team has confirmed that the switch-off command was executed without incident and the probe is operating normally.
In 2018, the plasma science instrument proved critical in determining that Voyager 2 left the heliosphere. The boundary between the heliosphere and interstellar space is demarcated by changes in the atoms, particles, and magnetic fields that instruments on the Voyagers can detect. Inside the heliosphere, particles from the Sun flow outward, away from our nearest star. The heliosphere is moving through interstellar space, so at Voyager 2’s position near the front of the solar bubble, the plasma flows in almost the opposite direction of the solar particles.
The plasma science instrument consists of four “cups.” Three cups point in the direction of the Sun and observed the solar wind while inside the heliosphere. A fourth points at a right angle to the direction of the other three and has observed the plasma in planetary magnetospheres, the heliosphere, and now, interstellar space.
When Voyager 2 exited the heliosphere, the flow of plasma into the three cups facing the Sun dropped off dramatically. The most useful data from the fourth cup comes only once every three months, when the spacecraft does a 360-degree turn on the axis pointed toward the Sun. This factored into the mission’s decision to turn this instrument off before others.
The plasma science instrument on Voyager 1 stopped working in 1980 and was turned off in 2007 to save power. Another instrument aboard Voyager 2, called the plasma wave subsystem, can estimate the plasma density when eruptions from the Sun drive shocks through the interstellar medium, producing plasma waves.
The Voyager team continues to monitor the health of the spacecraft and its available resources to make engineering decisions that maximize the mission’s science output.