

New research indicates that divergent mammalian groups have independently evolved similar inner ear shapes due to analogous ecological niches, underlining the adaptive nature of mammalian ear evolution.
A new study has shed light on the remarkably convergent evolution in the inner ear of mammals, revealing that a group of highly divergent mammals known as Afrotheria and distantly related, but ecologically very similar mammals independently evolved similar inner ear shapes.
The research, conducted by an international research team led by Nicole Grunstra from the University of Vienna and Anne Le Maître from the Konrad Lorenz Institute (KLI) for Evolution and Cognition Research (Klosterneuburg), was recently published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications.

Diversity and Adaptation of Inner Ears
The vertebrate inner ear, located inside the bony skull, is responsible for hearing and balance. Diversity in its complex shape among animals has long been thought to reflect adaptations to different environments and locomotor behaviors. At the same time, the shape of the inner ear also tracks evolutionary descent, with closely related species tending to have more similar inner ear shapes than distantly related species. This suggests that neutral (non-adaptive) evolution may be more important in shaping inner ear morphology than previously thought. The team’s new study on the inner ears of a diverse group of mammals provides novel insights into this issue.
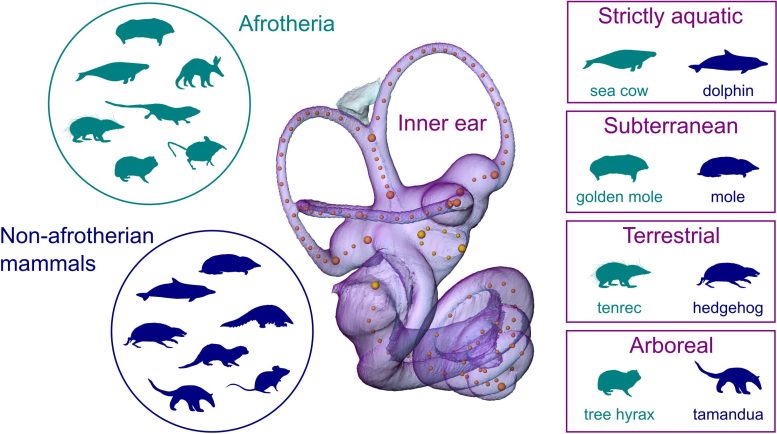
Methodology: 3D Ear Modeling
The team of evolutionary biologists and paleontologists, including researchers from the Natural History Museum Vienna, studied the shape of the inner ear in Afrotheria. This animal group consists of related mammals that are vastly different in their anatomy and habitats, including the aardvark, elephants, golden moles, hyraxes, rodent-like elephant shrews, and sea cows.
The researchers compared their ear shape to other mammals that are analogous in anatomy, ecology, and/or locomotor behavior, but are only very distantly related to them, such as anteaters, ‘true’ moles, rodents, hedgehogs, and dolphins. The team conducted X-ray microtomography on skulls housed in museum collections, from which they reconstructed virtual 3D models of the inner ear. They then compared inner ear shapes between afrotherians and their analogs and analyzed ear shape in relation to habitat and locomotion.
Patterns of Independent Evolution
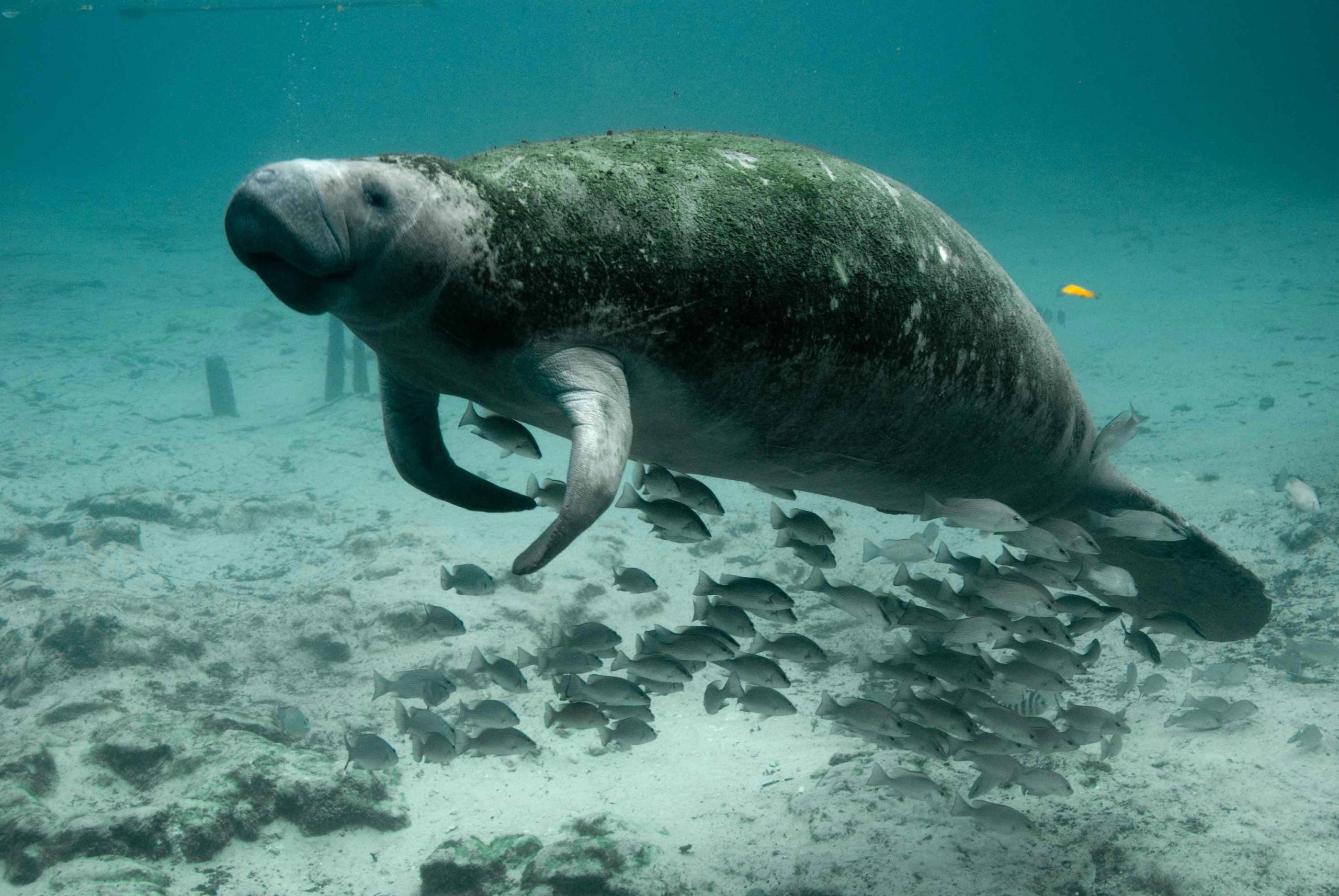
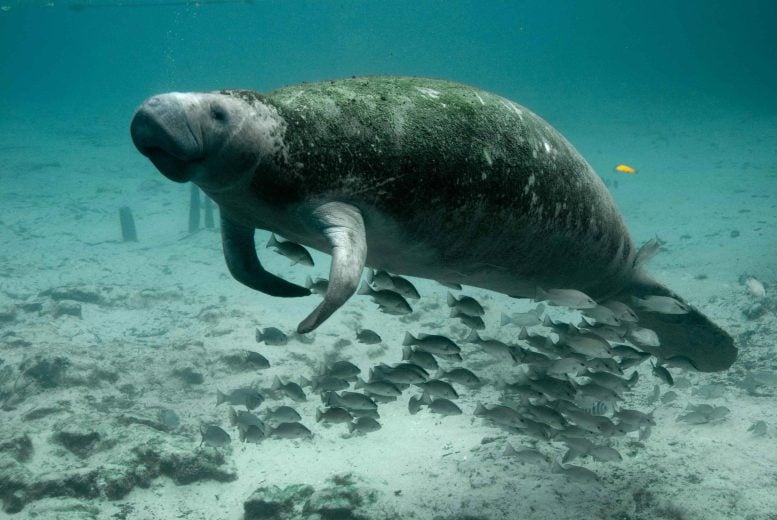
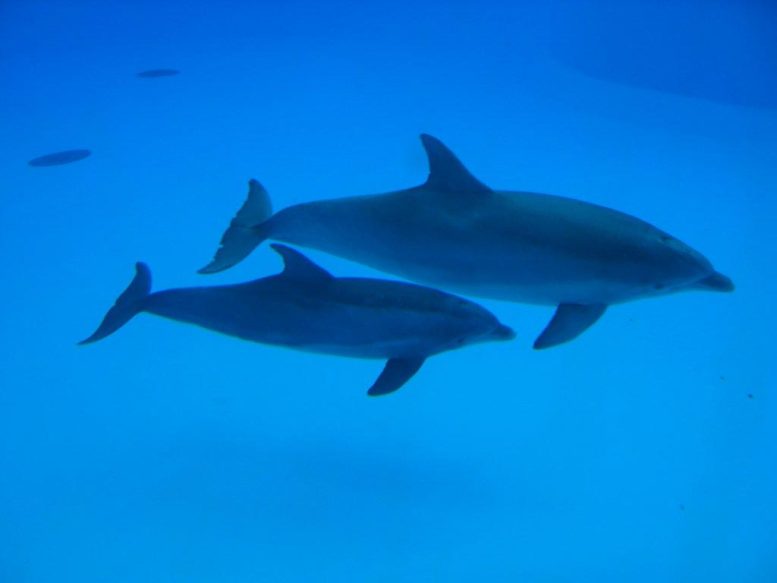
“We found that the inner ear shape is more similar between analogous species than between non-analogous ones, even when the latter share a more recent common ancestor and are therefore more closely related,” explains first author Nicole Grunstra from the University of Vienna. For instance, the ear shape of sea cows is less like that of elephants or hyraxes (closely related afrotherians) and more like that of a dolphin (a much more distantly related mammal). This shape similarity corresponds to adaptations to a strictly aquatic environment.
The study also found similar ear shapes in other distantly related species with the same environment or feeding strategy, for example in subterraneous species, or species living in trees. “We were also able to show that eco-morphologically similar mammals evolved similar ear shapes as an adaptation to shared ecological niches or locomotion, rather than by chance,” interprets senior author Anne Le Maître. This is strong evidence for convergent evolution, a process during which ancestrally different ear shapes independently evolve to be similar because of shared selection pressures.
Evolvability and Adaptation in Mammalian Ear
The new study seemingly contradicts recent work on birds, reptiles, and certain mammals that have cast doubt on the extent to which adaptive processes have shaped inner ear variation in vertebrates. One explanation is that adaptive differences in ear shape likely play out particularly strongly when comparing species with diverse ecological strategies, such as afrotherians and many other mammals. Another possible explanation is that the mammalian ear has higher ‘evolvability’, which is the intrinsic capacity for adaptive evolution.
Among vertebrates, the mammalian ear is particularly complex. Compared to birds, crocodiles or lizards, the mammalian ear acquired several extra components through the evolutionary reduction and transformation of jaw bones and their subsequent integration into the middle ear (whereas in birds and reptiles these have remained part of the jaw). This peculiarity enables mammals to detect a much wider range of sounds, particularly high tones.
Importantly, it also increases the anatomical, genetic and developmental complexity of the ear, which theory predicts widens the range of potential ear shapes that can evolve. “An increase in genetic and developmental factors of a trait gives natural selection more knobs to turn, which facilitates the evolution of different adaptations,” adds co-senior author Philipp Mitteröcker from the University of Vienna. This increased evolvability of the ear may have helped pave the way for adaptations to new environments and locomotor behaviors during mammalian evolution.
Reference: “Convergent evolution in Afrotheria and non-afrotherians demonstrates high evolvability of the mammalian inner ear” by Nicole D. S. Grunstra, Fabian Hollinetz, Guillermo Bravo Morante, Frank E. Zachos, Cathrin Pfaff, Viola Winkler, Philipp Mitteroecker and Anne Le Maître, 16 September 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52180-1
This study was funded by the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF).

