
Modern life relies on plastic. This lightweight, adaptable product is a cornerstone of packaging, medical equipment, the aerospace and automotive industries and more. But plastic waste remains a problem as it degrades in landfills and pollutes oceans.
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers have created a potential alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastic that is made from carbon dioxide (CO2) and lignin, a component of wood that is a low-cost byproduct of paper manufacturing and biofuel production. Their research was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
“Our study takes the harmful greenhouse gas CO2 and makes it into a useful raw material to produce degradable polymers or plastics,” said Hoyong Chung, an associate professor in chemical and biomedical engineering at the college. “We are not only reducing CO2 emissions, but we are producing a sustainable polymer product using the CO2.”
This study is the first to demonstrate the direct synthesis of what’s known as a cyclic carbonate monomer—a molecule made of carbon and oxygen atoms that can be linked with other molecules—made from CO2 and lignin.
By linking multiple monomers together, scientists can create synthetic polymers, long-chained molecules that can be designed to fill all manner of applications.
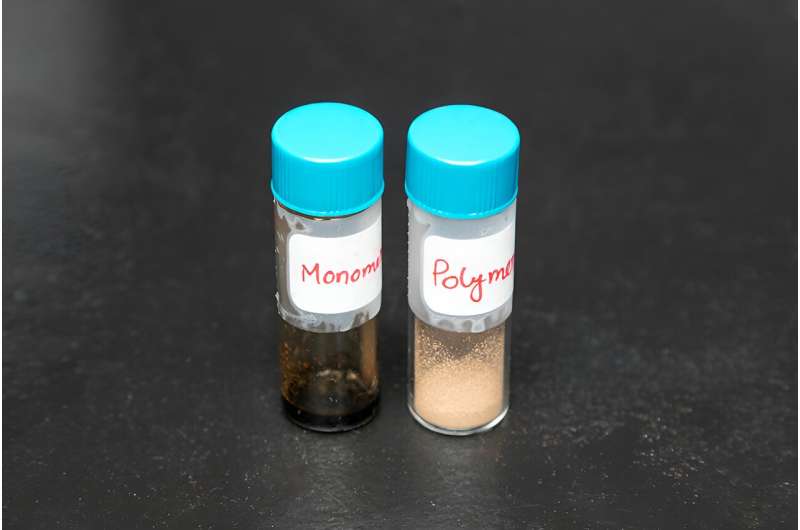

The material developed by Chung and his research team is fully degradable at the end of its life without producing microplastics and toxic substances. It can be synthesized at lower pressures and temperatures. And the polymer can be recycled without losing its original properties.
Using depolymerization, the researchers can convert polymers to pure monomers, which are the building blocks of polymers. This is the key to the high quality of the recycled material. The monomers can be recycled indefinitely and produce a high-quality polymer as good as the original, an improvement over previously developed and currently used polymer materials in which repeated heat exposure from melting reduces quality and allows for limited recycling.
“We can readily degrade the polymer via depolymerization, and the degraded product can synthesize the same polymer again,” Chung said. “This is more cost-effective and keeps it from losing original properties of polymers over multiple recycling. This is considered a breakthrough in material science, as it enables the realization of a true circular economy.”
The newly developed material could be used for low-cost, short-lifespan plastic products in such sectors as construction, agriculture, packaging, cosmetics, textiles, diapers and disposable kitchenware. With further development, Chung anticipates its use in highly specialized polymers for biomedical and energy storage applications.
Postdoctoral researcher Arijit Ghorai was the lead author of the study.
More information:
Arijit Ghorai et al, CO2 and Lignin‐Based Sustainable Polymers with Closed‐Loop Chemical Recycling, Advanced Functional Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202403035
Provided by
Florida State University
Citation:
Using CO₂ and biomass, researchers find path to more environmentally friendly recyclable plastics (2024, April 10)
retrieved 10 April 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-co8322-biomass-path-environmentally-friendly.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.