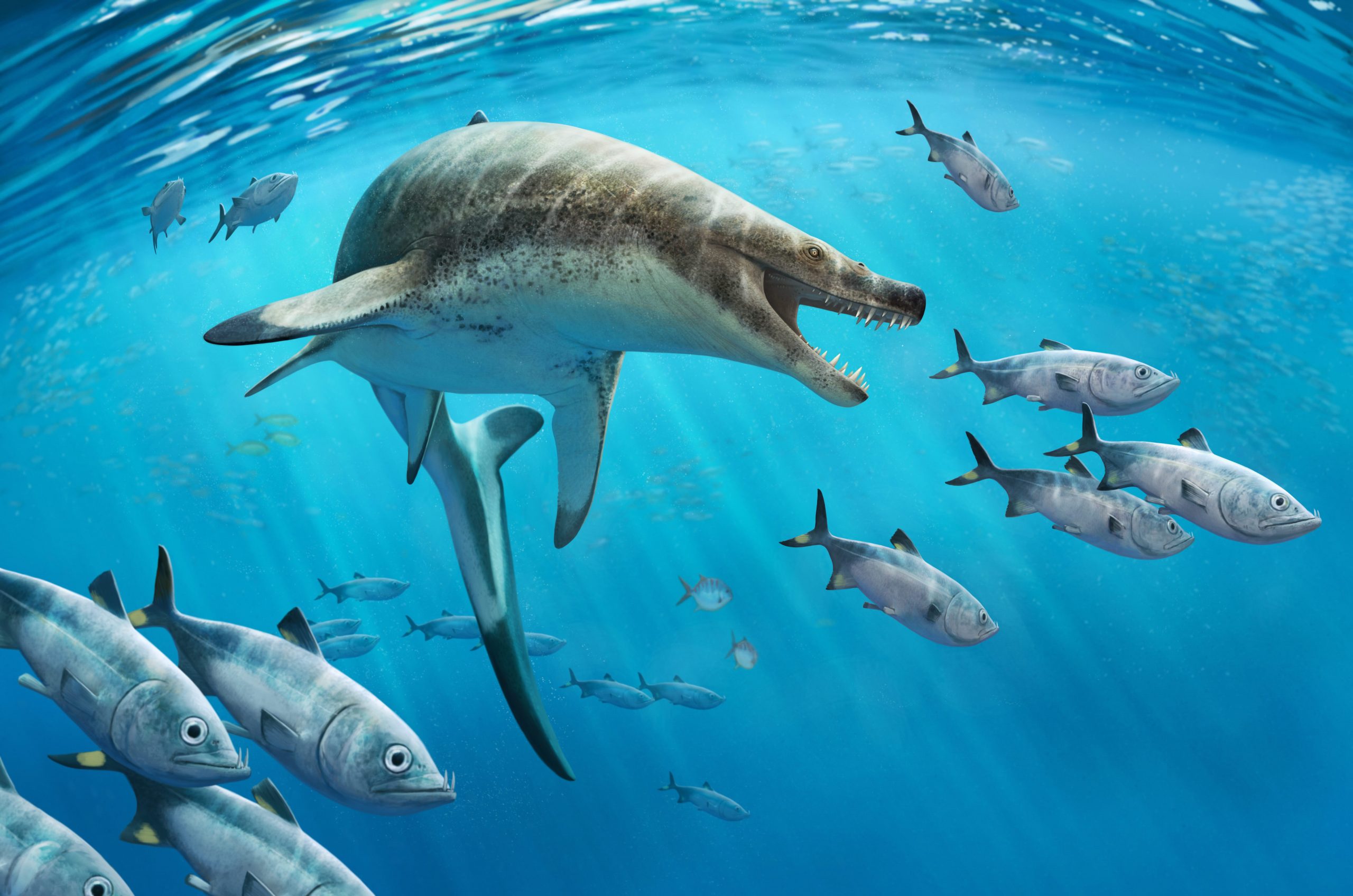
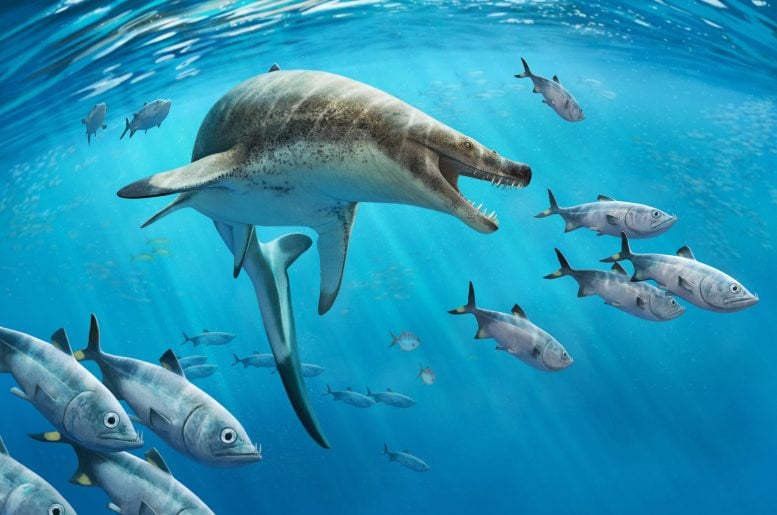
Researchers have discovered a new species of marine lizard, Khinjaria acuta, from the late Cretaceous period, showcasing the diversity of marine ecosystems before the dinosaur extinction. This species, part of the mosasaur family, highlights a time when the oceans teemed with a variety of giant predators, unlike today’s ecosystems dominated by a few apex predators. Credit: Andrey Atuchin
Sixty-six million years ago, the oceans were full of large apex predators, unlike now.
Paleontologists have discovered a strange new species of marine lizard with dagger-like teeth that lived near the end of the age of dinosaurs. Their findings, published in Cretaceous Research, show a dramatically different ocean ecosystem to what we see today, with numerous giant top predators eating large prey, unlike modern ecosystems where a few apex predators – such as great white sharks, orca, and leopard seals – dominate.
Khinjaria acuta was a member of the family Mosasauridae, or mosasaurs. Mosasaurs weren’t dinosaurs, but giant marine lizards, relatives of today’s Komodo dragons and anacondas, which ruled the oceans 66 million years ago, during the era of Tyrannosaurus and Triceratops.
Khinjaria had powerful jaws and long, dagger-like teeth to seize prey, giving it a nightmarish appearance. It was part of an extraordinarily diverse fauna of predators that inhabited the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Morocco, just before the dinosaurs went extinct.
International Collaboration and Diverse Predator Fauna
The study is based on a skull and parts of the skeleton collected from a phosphate mine southeast of Casablanca. The study involved researchers from the University of Bath in the UK, the Marrakech Museum of Natural History, the Museum National d’ Histoire Naturelle (NMNH) in Paris (France), Southern Methodist University in Texas (USA), and the University of the Basque Country (Bilbao).
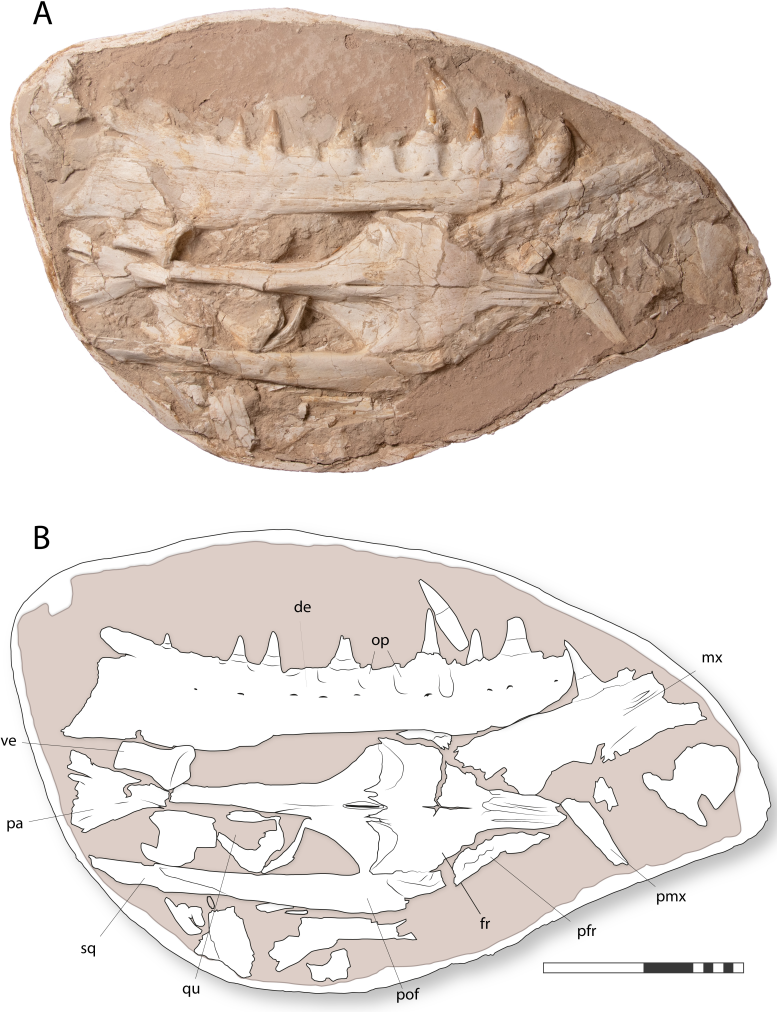
Fossil of Khinjaria acuta skull. Credit: University of Bath
“What’s remarkable here is the sheer diversity of top predators,” said Dr Nick Longrich of the Department of Life Sciences and the Milner Centre for Evolution at the University of Bath, who led the study. “We have multiple species growing larger than a great white shark, and they’re top predators, but they all have different teeth, suggesting they’re hunting in different ways.
“Some mosasaurs had teeth to pierce prey, others to cut, tear, or crush. Now we have Khinjaria, with a short face full of huge, dagger-shaped teeth. This is one of the most diverse marine faunas seen anywhere, at any time in history, and it existed just before the marine reptiles and the dinosaurs went extinct.”
A Rich, Pre-Extinction Ecosystem
Morocco’s diverse marine reptiles lived just before an asteroid struck the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico. Dust and fine particles shot into the high atmosphere blocked out the sun for months, causing darkness and cooling, which drove most of the planet’s species to extinction.
Dinosaurs were wiped out on land, and a handful of surviving species of mammals, birds, and lizards diversified to take their place. Meanwhile, the same happened in the oceans.
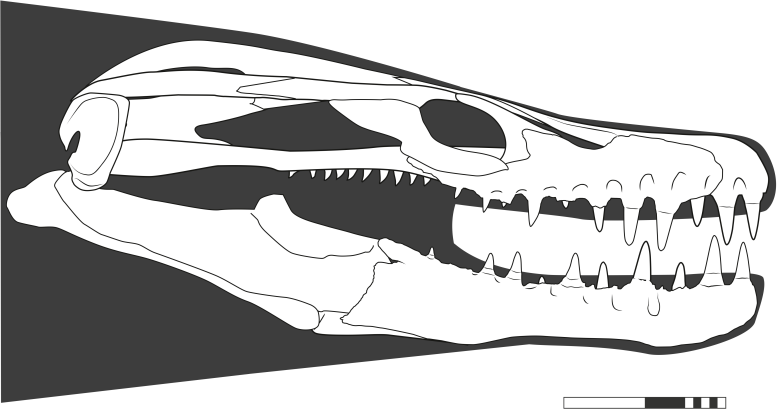
Khinjaria acuta skull reconstruction. Credit: Dr Nick Longrich
Mosasaurs, plesiosaurs, and giant sea turtles disappeared, along with entire families of fish. This opened the way for whales and seals, and fish like swordfish and tuna appeared. However, the ecosystem that evolved after the impact was different.
“There seems to have been a huge change in the ecosystem structure in the past 66 million years,” said Longrich. “This incredible diversity of top predators in the Late Cretaceous is unusual, and we don’t see that in modern marine communities.”
Modern marine food chains have just a few large apex predators, animals like orcas, white sharks, and leopard seals. The Cretaceous had a whole host of top predators.
Comparing Ancient and Modern Marine Ecosystems
Dr Longrich said: “It’s not just that we’re getting rid of the old actors and recasting new ones into the same roles. The story has changed dramatically.
“Modern ecosystems have predators like baleen whales and dolphins that eat small prey, and not many things eating large prey. The Cretaceous has a huge number of marine reptile species that take large prey. Whether there’s something about marine reptiles that caused the ecosystem to be different, or the prey, or perhaps the environment, we don’t know. But this was an incredibly dangerous time to be a fish, a sea turtle, or even a marine reptile.”
Professor Nathalie Bardet, from the NMNH, said: “The Phosphates of Morocco deposit in a shallow and warm epicontinental sea, under a system of upwellings; these zones are caused by currents of deep, cold, nutrient-rich waters rising towards the surface, providing food for large numbers of sea creatures and, as a result, supporting a lot of predators. This is probably one of the explanations for this extraordinary paleobiodiversity observed in Morocco at the end of the Cretaceous.”
“The phosphates of Morocco immerse us in the Upper Cretaceous seas during the latest geological times of the dinosaurs’ age. No deposit has provided so many fossils and so many species from this period”, said Professor NE. Jalil of NMNH. “After the’ titan of the seas’, Thalassotitan, the ‘saw-toothed’ mosasaur Xenodens, the ‘star-toothed’ mosasaur, Stelladens, and many others, now there is Khinjaria, a new mosasaur with dagger-like teeth.
“The elongation of the posterior part of the skull which accommodated the jaw musculature suggests a terrible biting force.”
Reference: “A bizarre new plioplatecarpine mosasaurid from the Maastrichtian of Morocco” by Nicholas R. Longrich, Michael J. Polcyn, Nour-Eddine Jalil, Xabier Pereda-Suberbiola and Nathalie Bardet, 1 March 2024, Cretaceous Research.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cretres.2024.105870
Funding: Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, European Regional Development Fund, Eusko Jaurlaritza, Euskal Herriko Unibertsitatea