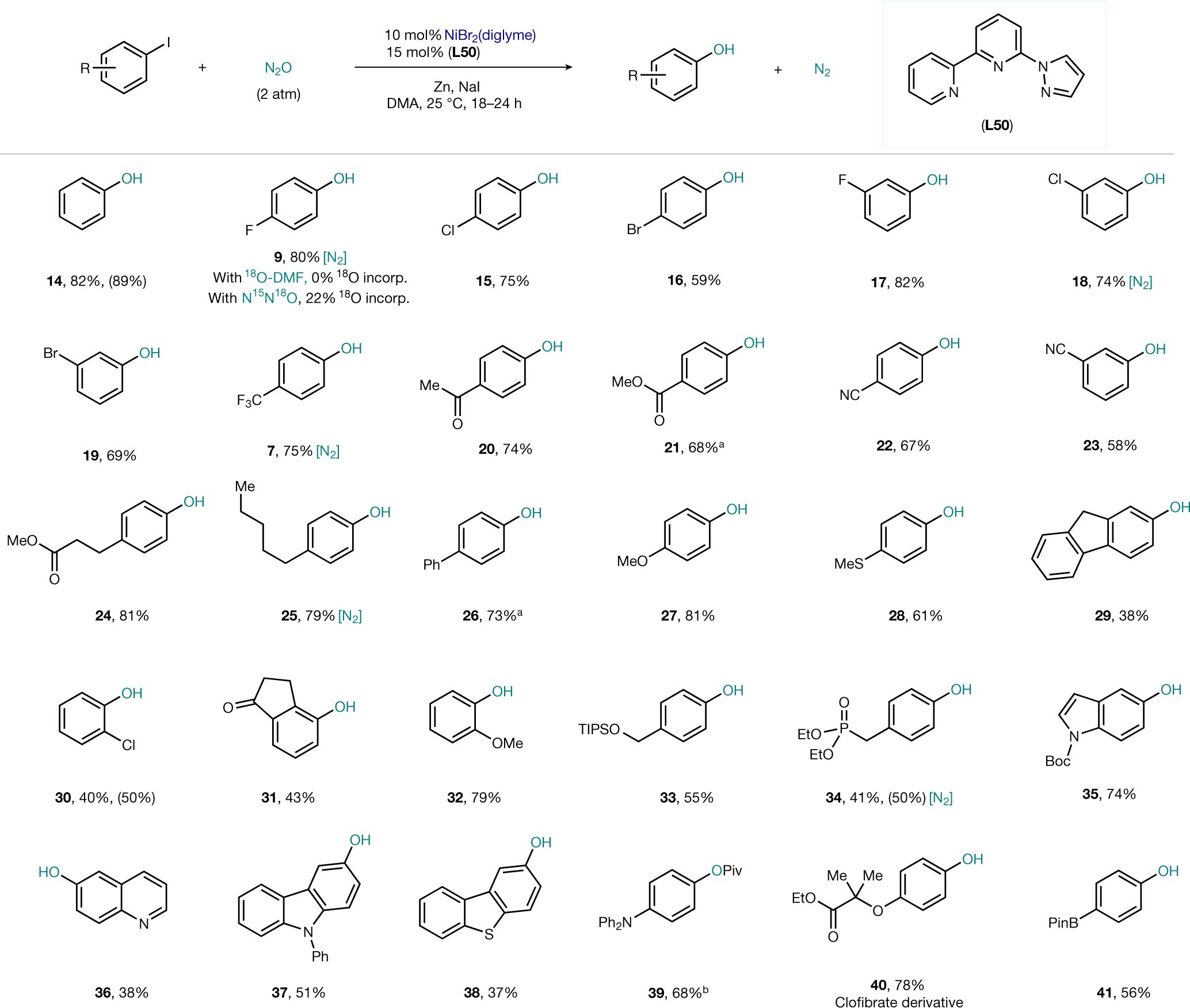
![Revalorization of N<sub>2</sub>O as O source in the catalytic synthesis of phenols. Scope of aryl iodides. [N<sub>2</sub>], N<sub>2</sub> detected by a gas chromatography–thermal conductivity detector at the end of the reaction. All yields are of isolated pure material. Yield in brackets: <sup>1</sup>H NMR yield calculated using dibromomethane as an internal standard. incorp., incorporated. See the Supplementary Information for details of the procedures. <sup>a</sup>Use of L18 as the ligand instead of L50. <sup>b</sup>Owing to the rapid oxidation of the free alcohol, 39 was obtained after quenching with Piv<sub>2</sub>O. Credit: <i>Nature</i> (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04516-4 Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide](https://skynews.icu/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Catalytic-synthesis-of-phenols-with-nitrous-oxide.jpg)
The emission of greenhouse gases threatens the global environment, and scientists around the world are increasingly committed to addressing this issue. While many research groups focus on carbon dioxide (CO2) or methane (CH4) revalorization strategies, a team led by Dr. Josep Cornellà at the Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung has focused on a lesser-known gas that also contributes significantly to global warming: nitrous oxide (N2O), also known as “laughing gas.”
Nitrous oxide has a global warming potential approximately 300 times higher than that of carbon dioxide, and is known to be an ozone depletion agent. As a result of human activities, emissions of nitrous oxide have increased by up to 2% in recent decades.
However, Josep Cornellà’s group considers this molecule far too valuable to be emitted into the atmosphere. N2O is indeed a great source of O atoms, and the byproduct generated is N2, molecular nitrogen, which is harmless. The challenge, however, was that for a long time, N2O was considered an inert gas requiring drastic measures to grab the O atom from its structure. However, in their work, now published in Nature, the team at the Cornellà Lab has shown that this can be achieved by reacting N2O with a simple catalyst under mild conditions to make phenols, valuable compounds for industry
“Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide” was published in Nature.
Climate-warming microbes thrive in drying peatlands
Franck Le Vaillant et al, Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide, Nature (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04516-4
Max Planck Society
Citation:
Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide (2022, May 9)
retrieved 9 May 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-05-catalytic-synthesis-phenols-nitrous-oxide.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.