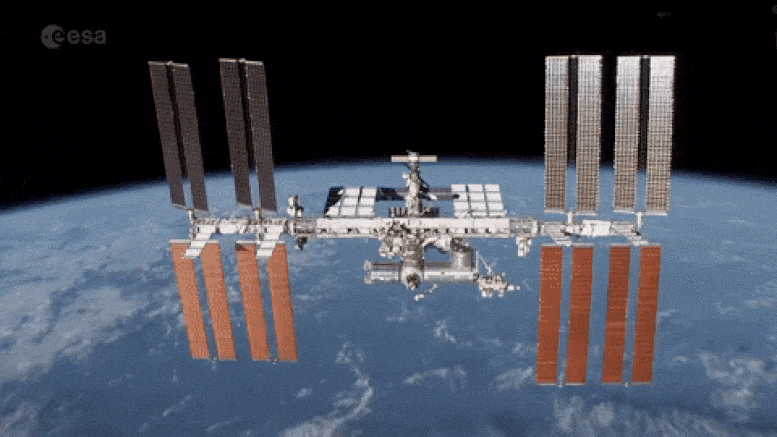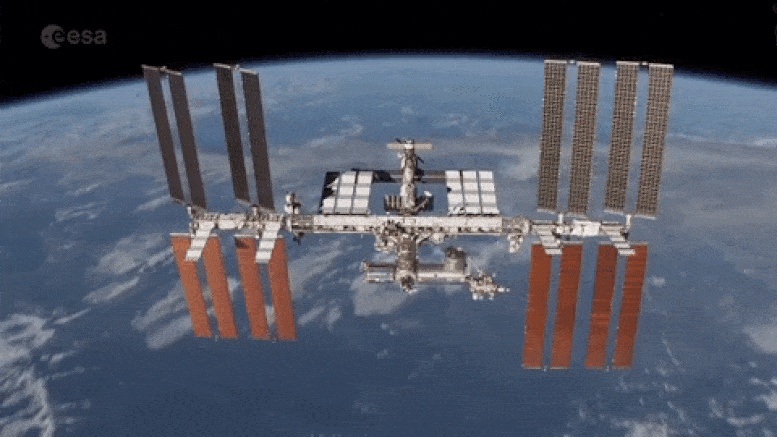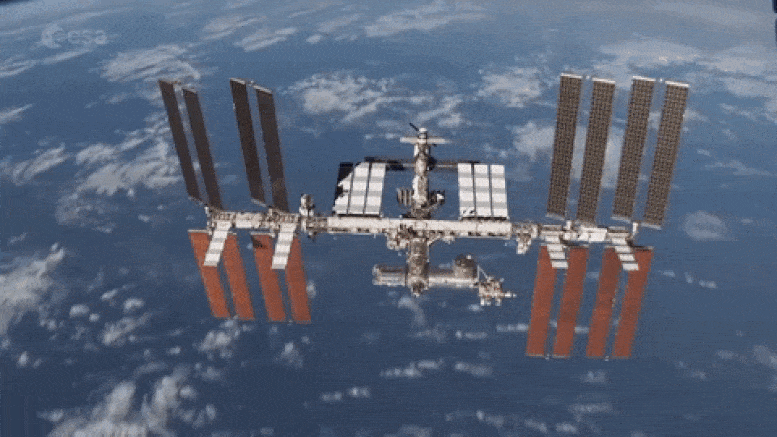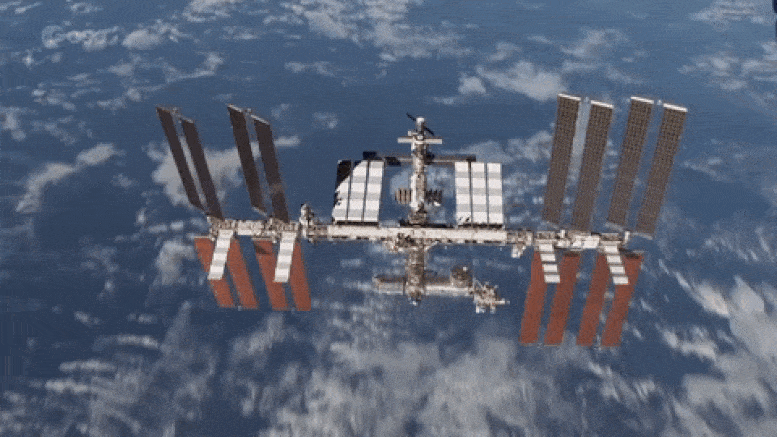

Monday November 2, 2020, marked 20 years since the first crew took up residence on the International Space Station. Since then the football field-sized feat of engineering has hosted 26 European missions and supported over 2700 international experiments to improve life on Earth and in space. Credit: ESA/NASA
The International Space Station (ISS) partners have committed to extending its operations, with the United States, Japan, Canada, and European Space Agency (ESA) countries supporting it until 2030, and Russia until 2028.
The ISS has been a unique platform for conducting cutting-edge science and research in microgravity for over 22 years, with 266 individuals from 20 countries conducting over 3,300 experiments in various scientific fields. As it enters its third decade, the focus is on maximizing scientific returns, with new benefits and innovative research emerging. The ISS is one of the most intricate international collaborations, with all partners crucial for its operation. Its continued presence aids NASA’s Artemis missions for long-term lunar exploration.
The International Space Station (ISS) partners have committed to extending the operations of this unique platform in low Earth orbit where, for more than 22 years, humans have lived and worked for the benefit of humanity, conducting cutting-edge science and research in microgravity. The United States, Japan, Canada, and the participating countries of ESA (European Space Agency) have confirmed they will support continued space station operations through 2030 and Russia has confirmed it will support continued station operations through 2028. NASA will continue to work with its partner agencies to ensure an uninterrupted presence in low Earth orbit, as well as a safe and orderly transition from the space station to commercial platforms in the future.
“The International Space Station is an incredible partnership with a common goal to advance science and exploration,” said Robyn Gatens, director of the International Space Station Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Extending our time aboard this amazing platform allows us to reap the benefits of more than two decades of experiments and technology demonstrations, as well as continue to materialize even greater discovery to come.”

The International Space Station photographed by Expedition 56 crew members from a Soyuz spacecraft after undocking on October 4, 2018. NASA astronauts Andrew Feustel and Ricky Arnold and Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Artemyev executed a fly around of the orbiting laboratory to take pictures of the station before returning home after spending 197 days in space. Credit: NASA/Roscosmos
Since its launch in 1998, the International Space Station has been visited by 266 individuals from 20 countries. The space station is a unique scientific platform where crew members conduct experiments across multiple disciplines of research, including Earth and space science, biology, human physiology, physical sciences and technology demonstrations that could not be done on Earth. The crew living aboard the station are the hands of thousands of researchers on the ground conducting more than 3,300 experiments in microgravity. Now, in its third decade of operations, the station is in the decade of results when the platform can maximize its scientific return. Results are compounding, new benefits are materializing, and innovative research and technology demonstrations are building on previous work.
The space station is one of the most complex international collaborations ever attempted. It was designed to be interdependent, relies on contributions from across the partnership to function, and no partner currently has the capability to operate the space station without the other.
With a continued foothold in low Earth orbit, NASA’s Artemis missions are underway, setting up a long-term presence at the Moon for science and exploration.