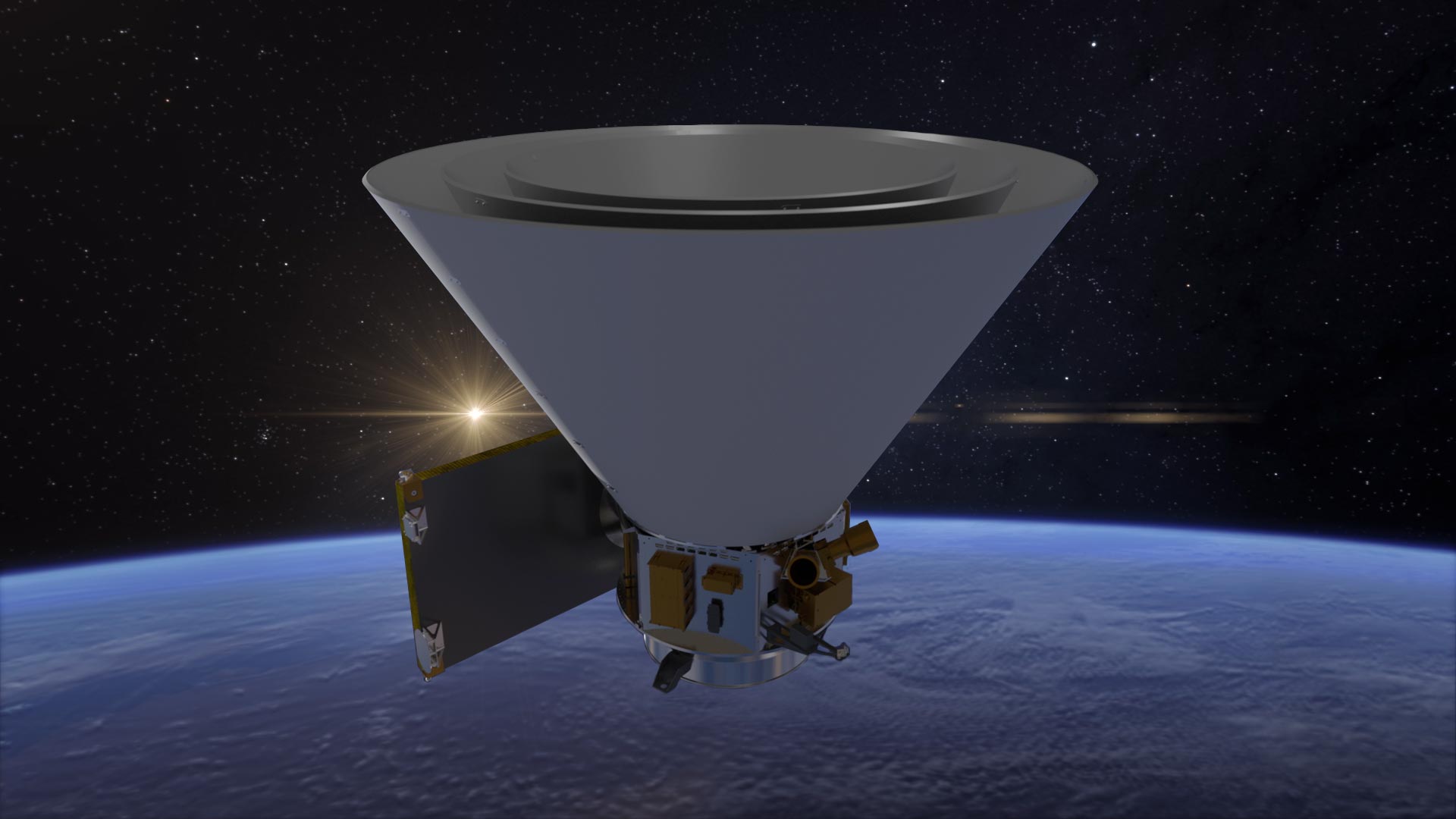
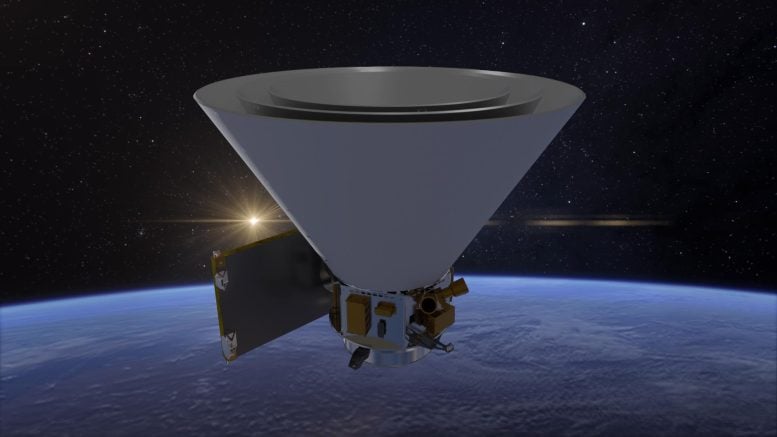


Launching by 2025, NASA’s SPHEREx mission will map hundreds of millions of galaxies in 102 infrared colors to investigate the universe’s expansion, galaxy light emissions, and key molecules necessary for life, enhancing our cosmic understanding.
Launching by April 2025, NASA’s SPHEREx mission will not be the first space telescope to observe hundreds of millions of stars and galaxies, but it will be the first to do so in 102 infrared colors. Although these colors are invisible to the human eye, scientists will use SPHEREx’s infrared data to explore questions ranging from the physics that shaped the universe in its first moments to the origins of water on planets like Earth.
“We are the first mission to look at the whole sky in so many colors,” said SPHEREx Principal Investigator Jamie Bock, who is based jointly at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Caltech, both in Southern California. “Whenever astronomers look at the sky in a new way, we can expect discoveries.”
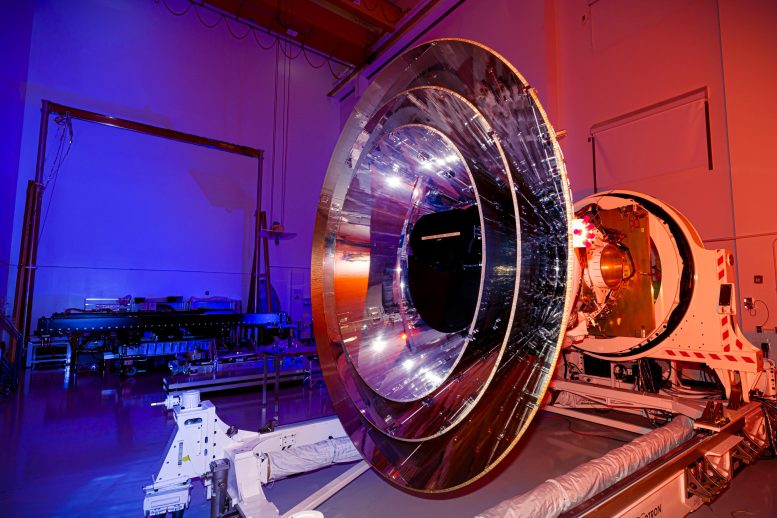
SPHEREx, which stands for Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer, will collect infrared light with wavelengths slightly longer than those visible to the human eye. The telescope will use spectroscopy to break down the light from millions of stars and galaxies into distinct colors, much like a prism turning sunlight into a rainbow. This detailed color analysis can reveal an object’s composition, its distance from Earth, and other key properties.
Here are the three major scientific investigations that SPHEREx will carry out using its all-sky infrared map.
Cosmic Origins
What human eyes perceive as colors are distinct wavelengths of light. The only difference between colors is the distance between the crests of the light wave. If a star or galaxy is moving, its light waves get stretched or compressed, changing the colors they appear to emit. (It’s the same with sound waves, which is why the pitch of an ambulance siren seems to go up as its approaches and lowers after it passes.) Astronomers can measure the degree to which light is stretched or compressed and use that to infer the distance to the object.
SPHEREx will apply this principle to map the position of hundreds of millions of galaxies in 3D. By doing so, scientists can study the physics of inflation, the event that caused the universe to expand by a trillion-trillion fold in less than a second after the big bang. This rapid expansion amplified small differences in the distribution of matter. Because these differences remain imprinted on the distribution of galaxies today, measuring how galaxies are distributed can tell scientists more about how inflation worked.
Galactic Origins
SPHEREx will also measure the collective glow created by all galaxies near and far — in other words, the total amount of light emitted by galaxies over cosmic history. Scientists have tried to estimate this total light output by observing individual galaxies and extrapolating to the trillions of galaxies in the universe. But these counts may leave out some faint or hidden light sources, such as galaxies too small or too distant for telescopes to easily detect.
With spectroscopy, SPHEREx can also show astronomers how the total light output has changed over time. For example, it may reveal that the universe’s earliest generations of galaxies produced more light than previously thought, either because they were more plentiful or bigger and brighter than current estimates suggest. Because light takes time to travel through space, we see distant objects as they were in the past. And, as light travels, the universe’s expansion stretches it, changing its wavelength and its color. Scientists can therefore use SPHEREx data to determine how far light has traveled and where in the universe’s history it was released.
Water’s Origins
SPHEREx will measure the abundance of frozen water, carbon dioxide, and other essential ingredients for life as we know it along more than 9 million unique directions across the Milky Way galaxy. This information will help scientists better understand how available these key molecules are to forming planets. Research indicates that most of the water in our galaxy is in the form of ice rather than gas, frozen to the surface of small dust grains. In dense clouds where stars form, these icy dust grains can become part of newly forming planets, with the potential to create oceans like the ones on Earth.
The mission’s colorful view will enable scientists to identify these materials, because chemical elements and molecules leave a unique signature in the colors they absorb and emit.
Big Picture
Many space telescopes, including NASA’s Hubble and James Webb, can provide high-resolution, in-depth spectroscopy of individual objects or small sections of space. Other space telescopes, like NASA’s retired Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), were designed to take images of the whole sky. SPHEREx combines these abilities to apply spectroscopy to the entire sky.
By combining observations from telescopes that target specific parts of the sky with SPHEREx’s big-picture view, scientists will get a more complete — and more colorful — perspective of the universe.
More About SPHEREx
SPHEREx, managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) for NASA’s Astrophysics Division, is a groundbreaking space mission designed to explore the cosmos in unprecedented detail using infrared spectroscopy. Built by BAE Systems (formerly Ball Aerospace), SPHEREx combines a telescope and spacecraft bus to gather data from across the universe. A global team of scientists from 10 institutions in the U.S. and South Korea will lead the science analysis, while data processing and archiving will be handled by IPAC at Caltech. With a principal investigator based at Caltech and JPL, SPHEREx aims to create a publicly accessible, colorful map of the universe to help unravel the mysteries of cosmic origins, galaxy formation, and essential life ingredients.