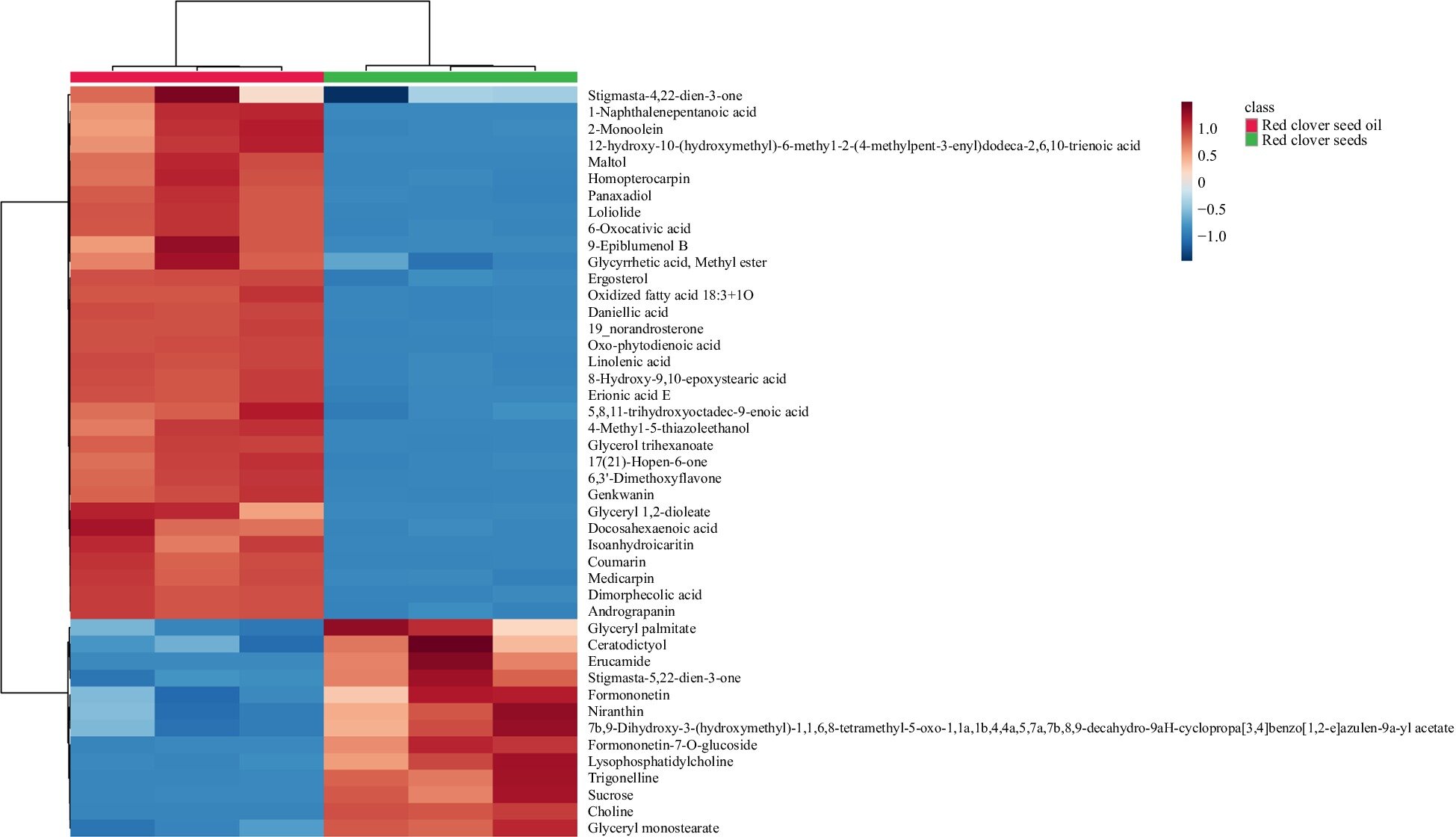
A research team has identified a wealth of bioactive compounds in red clover (Trifolium pratense) seeds and their oil, positioning them as a promising source for functional ingredients in food and health care products. Researchers reveal that red clover seed oil contains high concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids, phenolic compounds, and tocopherols, opening doors for potential pharmaceutical and nutritional applications.
Red clover, a flowering plant in the Fabaceae family, is widely grown across temperate regions and known for its nitrogen-fixing ability, enriching soil fertility. It has been valued for its potential in sustainable agriculture and as a cover crop to prevent soil erosion and reduce pesticide use.
However, its seeds—commonly used for animal feed—have received little attention for their potential health benefits. While extracts of red clover flowers have been used to treat various health conditions such as menopausal symptoms and cardiovascular diseases, little research has been conducted on the bioactive compounds present in red clover seeds.
A study published in Food Innovation and Advances suggests that red clover seed oil could serve as a functional ingredient in health-promoting foods or pharmaceuticals.
The research team used supercritical CO2 extraction to extract oil from red clover seeds. They used advanced metabolomics techniques to analyze the chemical composition of red clover seeds (RCS), focusing on proteins, sugars, organic acids, phenolic compounds, and fatty acids.
Proteins were found at 6.9 g/100 g of dry matter, while sugars, primarily sucrose and fructose, accounted for 77% and 14% of total sugars, respectively. These sugars contribute to gut health by promoting beneficial microbes.
Additionally, red clover seeds were rich in phenolic compounds such as flavanonols and flavonols, which are known for their antioxidant and anti-cancer properties. The most abundant phenolic compounds identified were taxifolin hexoside and quercetin, both contributing to cardiovascular health and oxidative stress reduction.
Furthermore, the seeds contained 7.0 g/100 g of lipids, with polyunsaturated fatty acids making up 79% of the total, including linoleic acid (72%). These fatty acids play significant roles in reducing inflammation and supporting heart health.
Tocopherols, predominantly alpha-tocopherol (97%), were also identified, showing promise as antioxidants. The use of supercritical CO2 extraction yielded an oil rich in bioactive lipids and unsaturated fatty acids, making red clover seed oil a potential ingredient for functional foods and pharmaceuticals due to its health-promoting properties.
According to the study’s senior researcher, Dr. Baoru Yang, “This is the first detailed examination of red clover seeds and their oil using advanced metabolomics techniques. Our findings demonstrate the high nutritional and bioactive value of these seeds, particularly their rich content of unsaturated fatty acids, phenolic compounds, and tocopherols. Red clover seed oil could be a game-changer for functional foods and pharmaceuticals.”
This pioneering research marks the first comprehensive study of red clover seeds and their oil, uncovering a range of bioactive compounds that offer promising health benefits. With further exploration, red clover seed oil could become a valuable ingredient in the food and pharmaceutical industries, supporting human health and wellness.
More information:
Ying Zhou et al, Compositional characteristics of red clover (Trifolium pratense) seeds and supercritical CO2 extracted seed oil as potential sources of bioactive compounds, Food Innovation and Advances (2024). DOI: 10.48130/fia-0024-0002
Citation:
Red clover seed oil rich in bioactive compounds, study finds (2024, October 14)
retrieved 15 October 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-10-red-clover-seed-oil-rich.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.