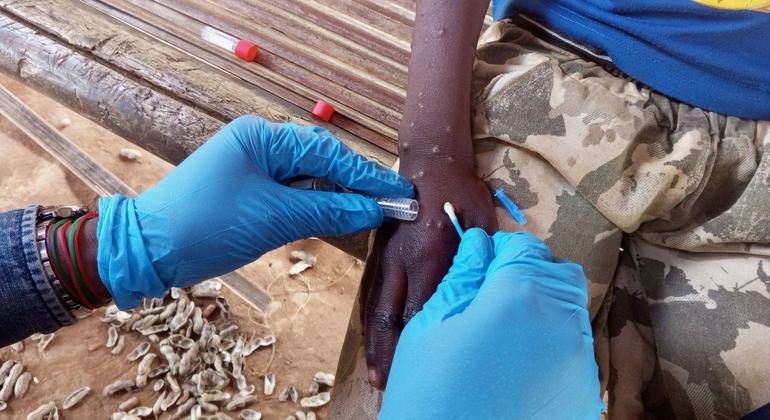

The Alinity m MPXV assay is a real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test that enables detection of monkeypox virus DNA from human skin lesion swabs.
It is manufactured by Abbott Molecular Inc, an American company, and specifically designed for use by trained clinical laboratory personnel.
‘A significant milestone’
“This first mpox diagnostic test listed under the Emergency Use Listing procedure represents a significant milestone in expanding testing availability in affected countries,” said Dr. Yukiko Nakatani, WHO Assistant Director-General for Access to Medicines and Health Products.
Detection of viral DNA by PCR testing is the gold standard for mpox diagnosis.
WHO said early diagnosis is critical as it enables timely treatment and care, as well as control of the virus.
Limited testing capacity and delays in confirming mpox cases persist in Africa, contributing to the continued spread of the virus.
Over 30,000 suspected cases have been reported on the continent this year, with the highest numbers in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Nigeria. Furthermore, only 37 per cent of suspected cases in DRC have been tested.
Global health emergency
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV). Symptoms include painful rash, enlarged lymph nodes, fever, headache and muscle ache.
A global outbreak first emerged in May 2022 which WHO said constituted a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) – the highest level of alarm under international health law.
Africa has seen an unprecedented increase and expansion in mpox cases this year, with transmission mainly centred in the DRC. The surge is being driven by two strains of the mpox virus, or clades.
Following rapid spread of the new virulent clade 1b strain, which has also been detected outside Africa, WHO on 14 August declared that mpox was once again a PHEIC.
Emergency Use Listing
WHO’s Emergency Use Listing (EUL) procedure accelerates the availability of life-saving medical products, such as vaccines, tests and treatments, in the context of a PHEIC.
On 28 August, the UN agency called on manufacturers to submit an expression of interest for EUL, recognizing the urgent need to strengthen global testing capacities as the virus continued to spread.
EUL is a risk-based procedure for assessing the quality, safety and performance of unlicensed vaccines, therapeutics and in vitro diagnostics, to expedite their availability during public health emergencies.
So far, WHO has received three additional submissions for EUL evaluation, and discussions are ongoing with other manufacturers.