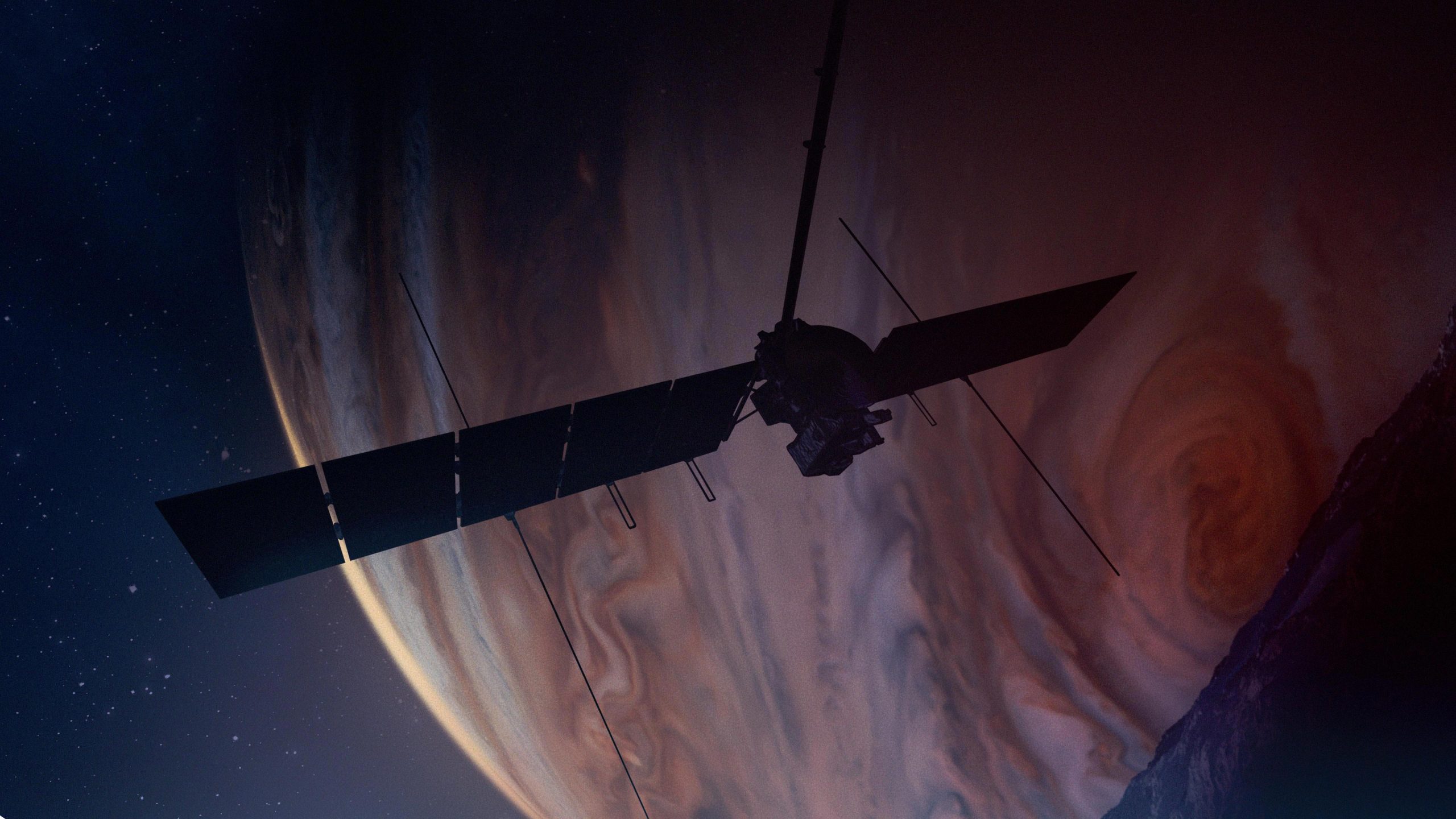


The first NASA spacecraft dedicated to studying an ocean world beyond Earth, Europa Clipper aims to find out if the ice-encased moon Europa could be habitable.
At an estimated cost of $5 billion, NASA’s Europa Clipper is set to embark on a pioneering 1.8 billion-mile journey to Jupiter’s moon Europa, aiming to explore its icy surface and underlying ocean to assess potential habitability. This ambitious mission, involving sophisticated science instruments and global collaboration, hopes to discover more habitable worlds within our solar system.
NASA’s Largest Planetary Mission
NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft, the largest the agency has ever built for a planetary mission, will travel 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers) from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Europa, an intriguing icy moon of Jupiter. The spacecraft’s launch period opens Thursday, October 10.
Data from previous NASA missions has provided scientists with strong evidence that an enormous salty ocean lies underneath the frozen surface of the moon. Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of the moon to gather data needed to determine whether there are places below its thick frozen crust that could support life.
Learn more about how NASA’s Europa Clipper came together – and how it will explore an ocean moon of Jupiter. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Here are eight things to know about the mission:
1. Europa is one of the most promising places to look for currently habitable conditions beyond Earth.
There’s scientific evidence that the ingredients for life — water, the right chemistry, and energy — may exist at Europa right now. This mission will gather the information scientists need to find out for sure. The moon may hold an internal ocean with twice the water of Earth’s oceans combined, and it may also host organic compounds and energy sources under its surface. If the mission determines that Europa is habitable, it would mean there may be more habitable worlds in our solar system and beyond than we have imagined.
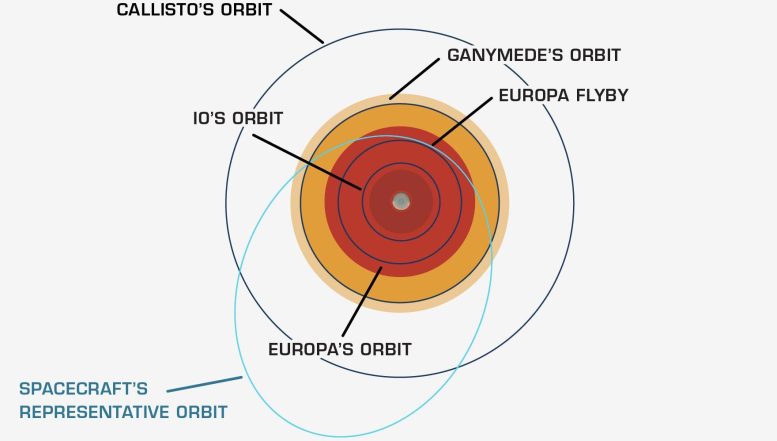
2. The spacecraft will fly through one of the most punishing radiation environments in our solar system — second only to the Sun’s.
Jupiter is surrounded by a gigantic magnetic field 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s. As the field spins, it captures and accelerates charged particles, creating radiation that can damage spacecraft. Mission engineers designed a spacecraft vault to shield sensitive electronics from radiation, and they plotted orbits that will limit the time Europa Clipper spends in most radiation-heavy areas around Jupiter.
3. Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter, studying Europa while flying by the moon dozens of times.
The spacecraft will make looping orbits around Jupiter that bring it close to Europa for 49 science-dedicated flybys. On each orbit, the spacecraft will spend less than a day in Jupiter’s dangerous radiation zone near Europa before zipping back out. Two to three weeks later, it will repeat the process, making another flyby.
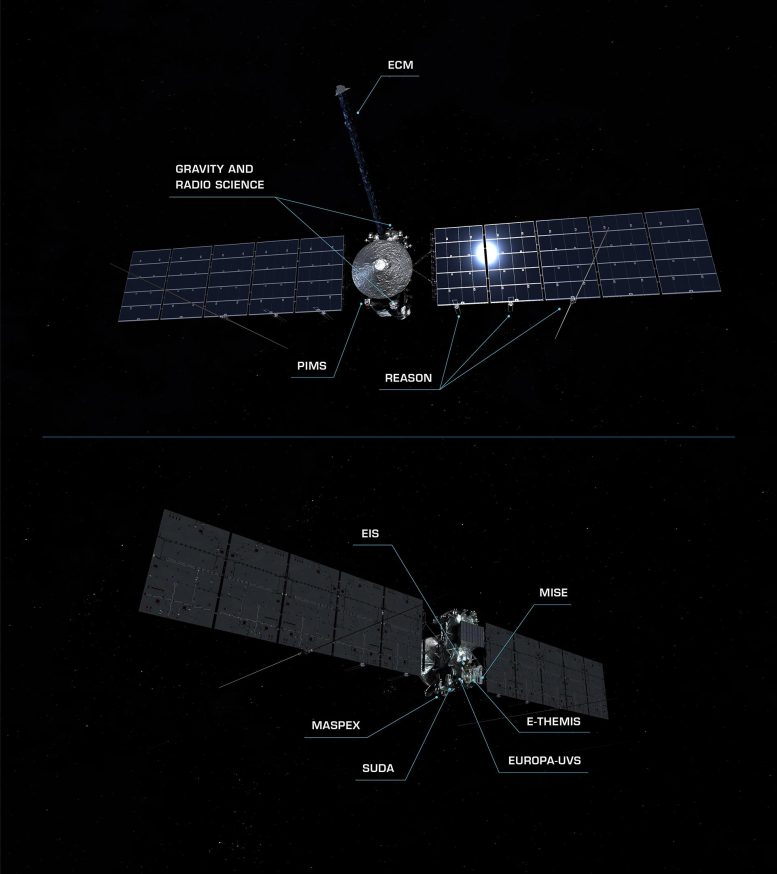

4. Europa Clipper features NASA’s most sophisticated suite of science instruments yet.
To determine if Europa is habitable, Europa Clipper must assess the moon’s interior, composition, and geology. The spacecraft carries nine science instruments and a gravity experiment that uses the telecommunications system. In order to obtain the best science during each flyby, all the science instruments will operate simultaneously on every pass. Scientists will then layer the data together to paint a full picture of the moon.
5. With antennas and solar arrays fully deployed, Europa Clipper is the largest spacecraft NASA has ever developed for a planetary mission.
The spacecraft extends 100 feet (30.5 meters) from one end to the other and about 58 feet (17.6 meters) across. That’s bigger than a basketball court, thanks in large part to the solar arrays, which need to be huge so they can collect enough sunlight while near Jupiter to power the instruments, electronics, and other subsystems.
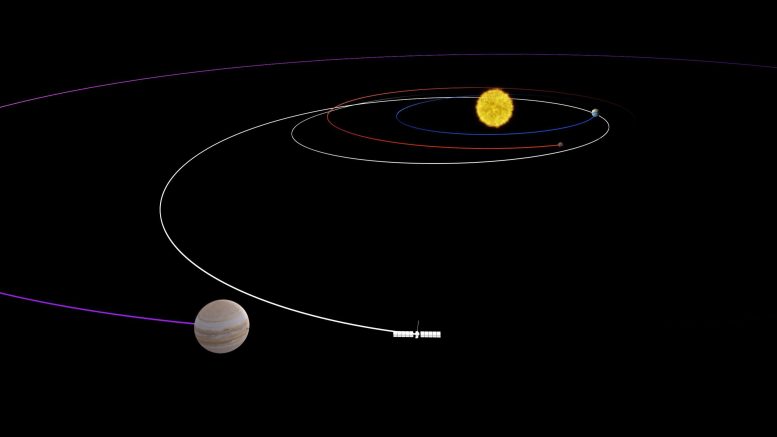
6. It’s a long journey to Jupiter.
Jupiter is on average some 480 million miles (about 770 million kilometers) from Earth; both planets are in motion, and a spacecraft can carry only a limited amount of fuel. Mission planners are sending Europa Clipper past Mars and then Earth, using the planets’ gravity as a slingshot to add speed to the spacecraft’s trek. After journeying about 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers) over 5½ years, the spacecraft will fire its engines to enter orbit around Jupiter in 2030.
7. Institutions across the U.S. and Europe have contributed to Europa Clipper.
Currently, about a thousand people work on the mission, including more than 220 scientists from both the U.S. and Europe. Since the mission was officially approved in 2015, more than 4,000 people have contributed to Europa Clipper, including teams who work for contractors and subcontractors.
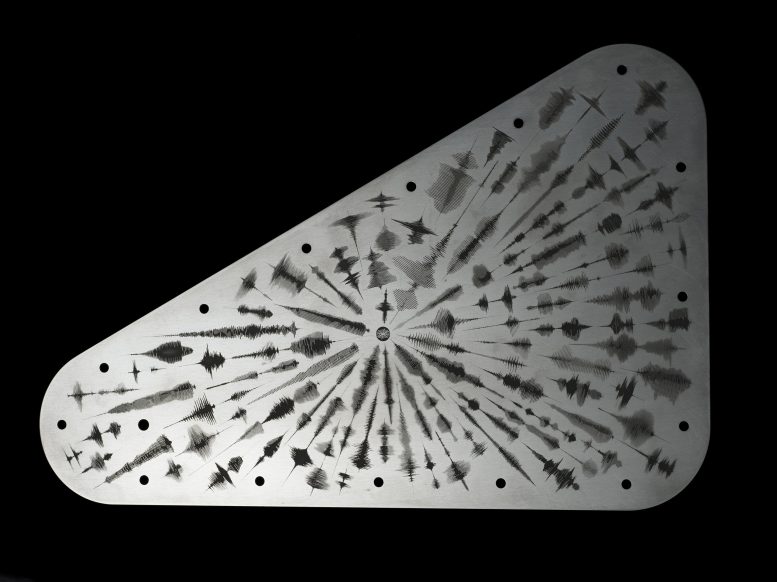
8. More than 2.6 million of us are riding along with the spacecraft, bringing greetings from one water world to another.
As part of a mission campaign called “Message in a Bottle,” the spacecraft is carrying a poem by U.S. Poet Laureate Ada Limón, cosigned by millions of people from nearly every country in the world. Their names have been stenciled onto a microchip attached to a tantalum metal plate that seals the spacecraft’s electronics vault. The plate also features waveforms of people saying the word “water” in over 100 spoken languages.
More About Europa Clipper
The Europa Clipper mission has three primary scientific goals: to measure the thickness of Europa’s icy shell and how it interacts with the ocean beneath, to analyze the moon’s composition, and to examine its geology. This in-depth exploration aims to advance our understanding of the potential for life on other worlds in our solar system.
The mission is led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), based in Pasadena, California, and developed in partnership with the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, under the oversight of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. The main body of the spacecraft was designed collaboratively by APL, JPL, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The Planetary Missions Program Office at Marshall manages the overall program.
The launch operations for the Europa Clipper are handled by NASA’s Launch Services Program at the Kennedy Space Center. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.