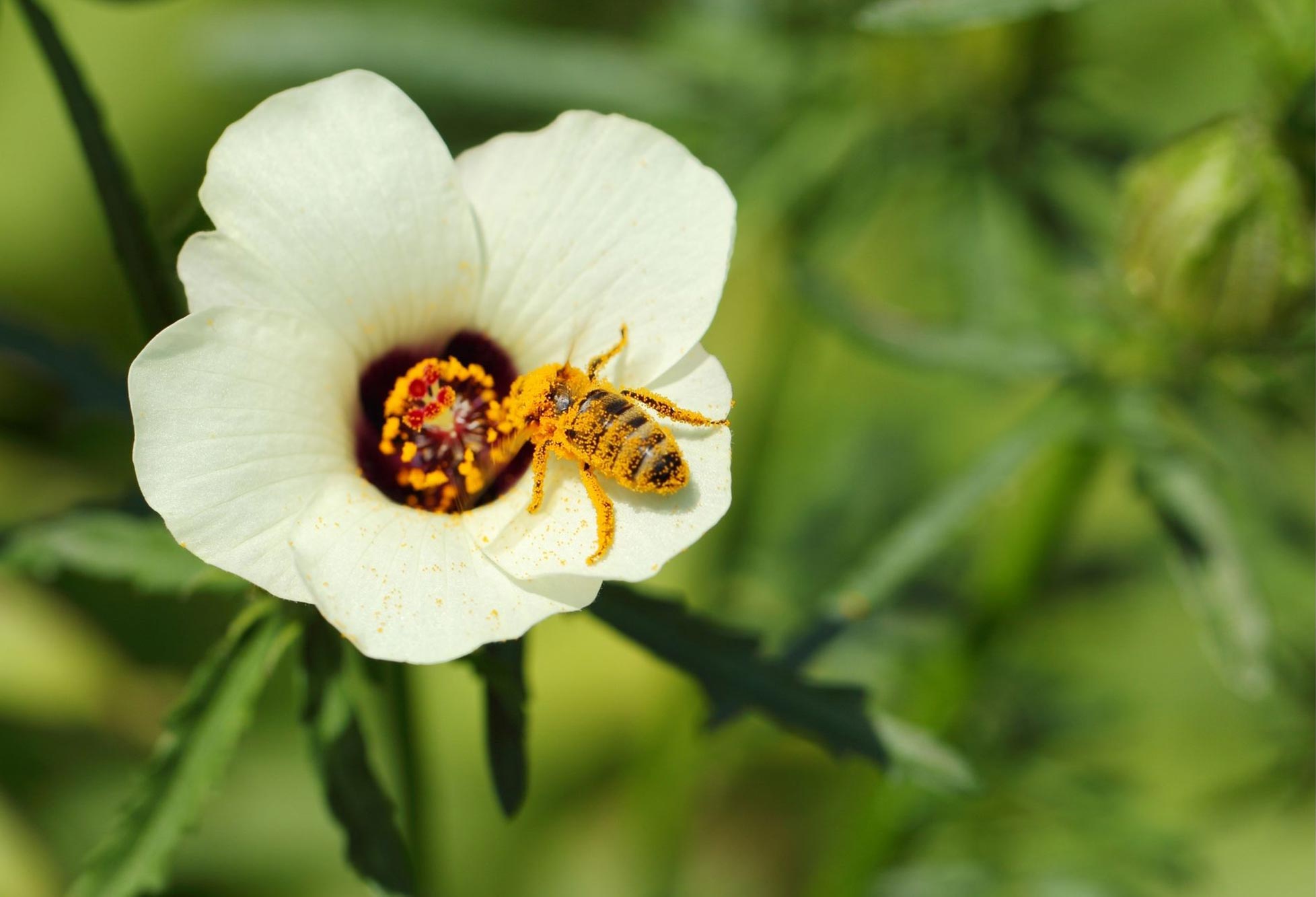


A study reveals that hibiscus flowers use pre-determined petal patterns to attract bees, who prefer larger bullseyes. These patterns are established early in the petal’s development and play a critical role in the plant’s pollination efficiency and evolutionary success.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge’s Sainsbury Laboratory have discovered that hibiscus flowers possess an invisible pre-pattern, established early in development, that dictates the size of the bullseyes on their petals- a key pattern that significantly impacts the flower’s ability to attract pollinating bees.
The study, recently published in Science Advances, also reveals that bees prefer larger bullseyes over smaller ones and fly 25% faster between artificial flower discs with larger bullseyes – potentially boosting efficiency for both bees and blossoms.

Experimental Study on Hibiscus Flower Patterns
Flower patterns help guide insects like bees to the center of the flower, where nectar and pollen await, increasing the plant’s chances of successful pollination. Despite their importance, surprisingly little is known about how these petal patterns form and how they have evolved into the vast diversity we see today, including spots, stripes, veins, and bullseyes.
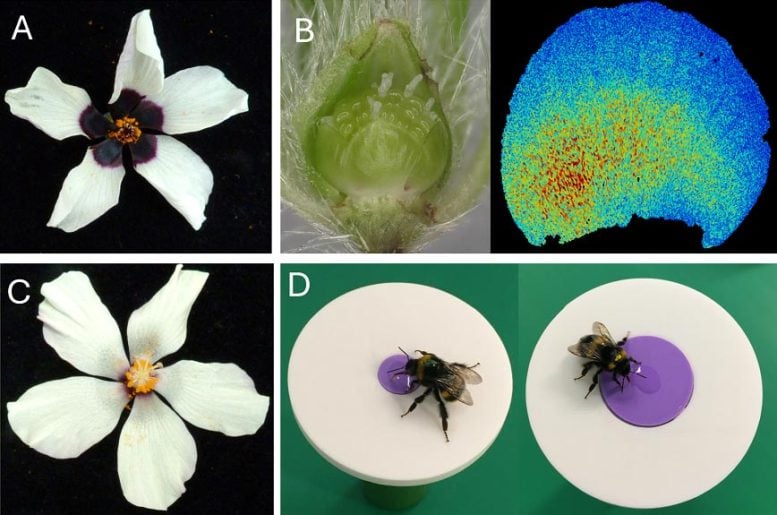
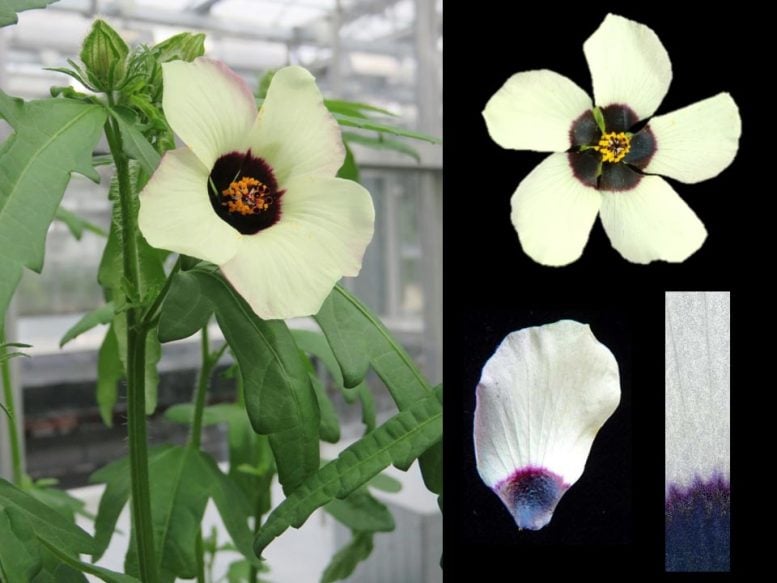
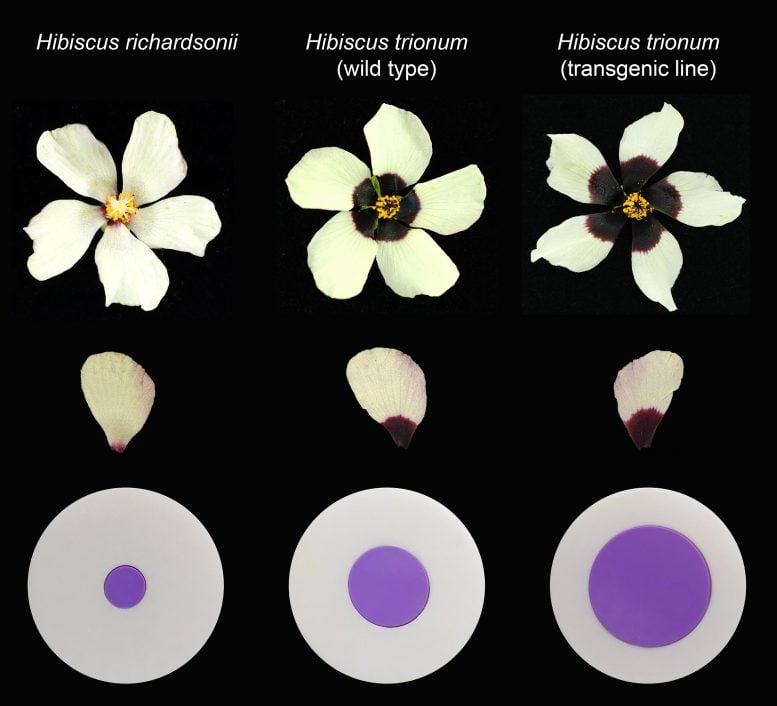
Using a small hibiscus plant as a model, researchers compared closely related plants with the same flower size but three differently sized bullseye patterns featuring a dark purple center surrounded by white – H. richardsonii (small bullseye covering 4% of the flower disc), H. trionum (medium bullseye covering 16%) and a transgenic line (mutation) of H. trionum (large bullseye covering 36%).
They found that a pre-pattern is set up on the petal surface very early in the flower’s formation, long before the petal shows any visible color. The petal acts like a ‘paint-by-numbers’ canvas, where different regions are predetermined to develop specific colors and textures long before they start looking different from one another.
The research also shows plants can precisely control and modify the shape and size of these patterns using multiple mechanisms, with possible implications for plant evolution. By fine-tuning these designs, plants may gain a competitive advantage in the contest to attract pollinators or maybe start attracting different species of insects.
Insights on Petal Pre-Patterning
“If a trait can be produced by different methods, it gives evolution more options to modify it and create diversity, similar to an artist with a large palette or a builder with an extensive set of tools. By studying how bullseye patterns change, what we are really trying to understand is how nature generates biodiversity,” explained Dr. Edwige Moyroud, who leads a research team studying the mechanisms underlying pattern formation in petals.
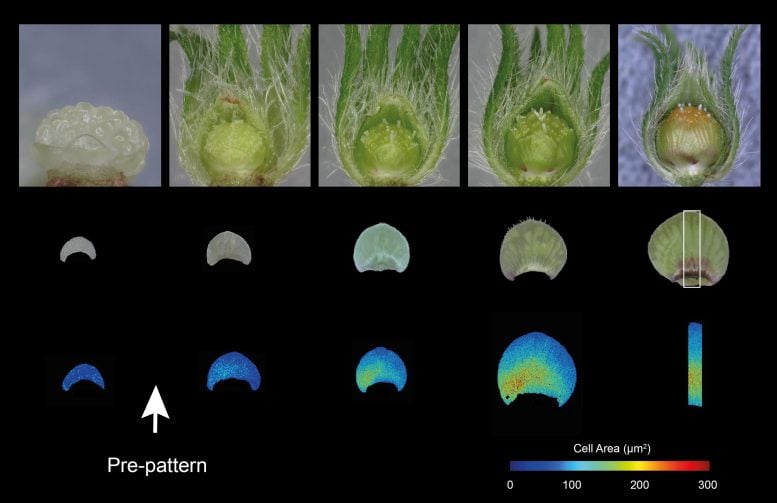
Lead author Dr. Lucie Riglet investigated the mechanism behind hibiscus petal patterning by analyzing petal development in the three hibiscus flowers that had the same total size but different bullseye patterns.
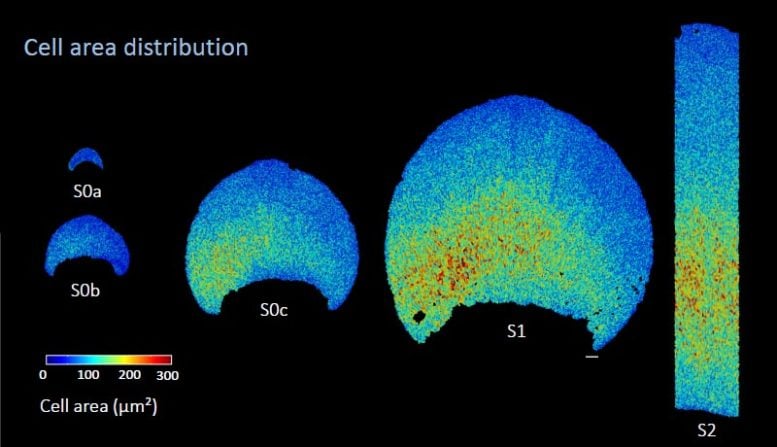
She found that the pre-pattern begins as a small, crescent-shaped region long before the bullseye is visible on tiny petals less than 0.2mm in size.

Dr. Riglet said: “At the earliest stage we could dissect, the petals have around 700 cells and are still greenish in color, with no visible purple pigment and no difference in cell shape or size. When the petal further develops to 4000 cells, it still does not have any visible pigment, but we identified a specific region where the cells were larger than their surrounding neighbors. This is the pre-pattern.”
These cells are important because they mark the position of the bullseye boundary, the line on the petal where the color changes from purple to white – without a boundary there is no bullseye.
Advanced Modeling and Impact on Pollination
A computational model developed by Dr. Argyris Zardilis provided further insights, and combining both computational models and experimental results, the researchers showed that hibiscus can vary bullseye dimensions very early during the pre-patterning phase or modulate growth in either region of the bullseye, by adjusting cell expansion or division, later in development.

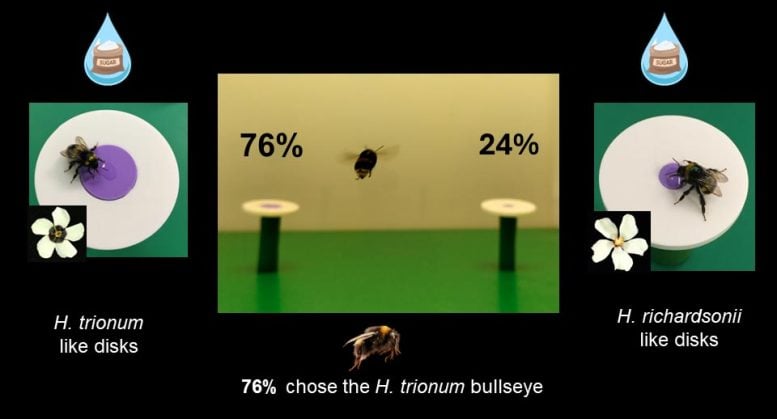
Dr. Riglet then compared the relative success of the bullseye patterns in attracting pollinators using artificial flower discs that mimicked the three different bullseye dimensions. Dr. Riglet explained: “The bees not only preferred the medium and larger bullseyes over the small bullseye, they were also 25% quicker visiting these larger flower discs. Foraging requires a lot of energy and so if a bee can visit 4 flowers rather than 3 flowers in the same time, then this is probably beneficial for the bee, and also the plants.”
Researchers compared the relative success of the bullseye patterns in attracting pollinators using artificial flower discs that mimicked the three different bullseye dimensions. The bees not only preferred the medium and larger bullseyes over the small bullseye, they were also 25% quicker visiting these larger flower discs. Credit: Lucie Riglet
Evolutionary Significance and Future Research
The researchers think that these pre-patterning strategies could have deep evolutionary roots, potentially influencing the diversity of flower patterns across different species. The next step for Edwige Moyroud’s research team is to identify the signals responsible for generating these early patterns and to explore whether similar pre-patterning mechanisms are used in other plant organs, such as leaves.
This research not only advances our understanding of plant biology but also highlights the intricate connections between plants and their environments, showing how precise natural designs can play a pivotal role in the survival and evolution of species.
For example, H. richardsonii, which has the smallest bullseye of the three hibiscus plants studied in this research, is a critically endangered plant native to New Zealand. H. trionum is also found in New Zealand, but is not considered to be native, and is widely distributed across Australia and Europe and has become a weedy naturalized plant in North America. Additional research is needed to determine whether the larger bullseye size helps H. trionum attract more pollinators and enhance its reproductive success.
Reference: “Hibiscus bullseyes reveal mechanisms controlling petal pattern proportions that influence plant-pollinator interactions” by Lucie Riglet, Argyris Zardilis, Alice L. M. Fairnie, May T. Yeo, Henrik Jönsson and Edwige Moyroud, 13 September 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp5574