

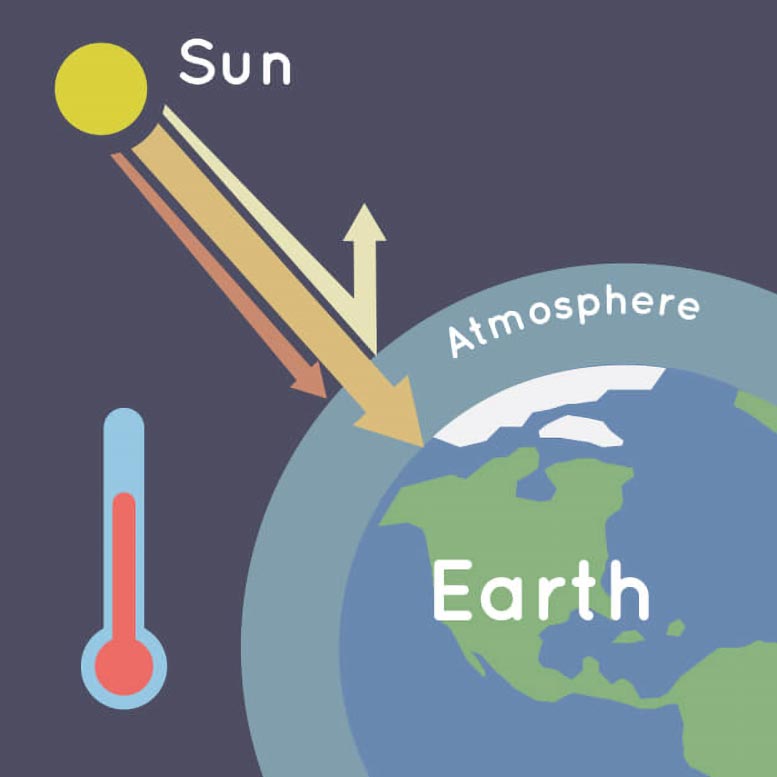
The greenhouse effect acts like a warm blanket around Earth, comprised of gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor that trap heat.
This natural phenomenon keeps the planet at an optimal temperature for life. However, human activities such as burning fossil fuels have intensified this effect, increasing carbon dioxide levels and thus, global temperatures, disrupting Earth’s energy balance and amplifying warming.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is the process through which heat is trapped near Earth’s surface by substances known as ‘greenhouse gases.’ Imagine these gases as a cozy blanket enveloping our planet, helping to maintain a warmer temperature than it would have otherwise.
Greenhouse gases consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor. Water vapor, which reacts to temperature changes, is referred to as a ‘feedback’, because it amplifies the effect of forces that initially caused the warming.
A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Carbon Dioxide’s Critical Role
Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of Earth’s atmosphere. If carbon dioxide were removed, the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse, and Earth’s surface temperature would drop significantly, by approximately 33°C (59°F).
The Goldilocks Planet
Greenhouse gases are part of Earth’s atmosphere. This is why Earth is often called the ‘Goldilocks’ planet – its conditions are just right, not too hot or too cold, allowing life to thrive. Part of what makes Earth so amenable is its natural greenhouse effect, which maintains an average temperature of 15 °C (59 °F) .
Human Impact and Climate Change
However, in the last century, human activities, primarily from burning fossil fuels that have led to the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, have disrupted Earth’s energy balance. This has led to an increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and ocean. The level of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere has been rising consistently for decades and traps extra heat near Earth’s surface, causing temperatures to rise.