
This article is an on-site version of our Europe Express newsletter. Premium subscribers can sign up here to get the newsletter delivered every weekday and Saturday morning. Standard subscribers can upgrade to Premium here, or explore all FT newsletters.
Good morning. A scoop to start: The EU could bar imports of coffee from a number of countries within weeks unless Brussels delays a ban on products from deforested areas, commodity companies and governments have warned.
Today, the head of the International Energy Agency tells our energy correspondent that Europe isn’t doing enough to protect Ukraine’s power infrastructure, and our competition correspondent reveals a demand from 20 EU capitals for the European Commission to cut more red tape than it has already promised.
Have a great weekend.
Cold comfort
The head of the IEA has accused Europe of being too reticent in its support for Ukraine, calling for more generators and repair equipment for the war-torn country ahead of a difficult winter, writes Alice Hancock.
Context: Ukraine has suffered heavy attacks on its energy infrastructure by Russia, particularly in late August in retaliation for its incursion into Russia’s Kursk region. Half of all Ukraine’s energy infrastructure has been destroyed, roughly equivalent to the capacity of Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia.
In a report published yesterday, the IEA said Ukraine’s electricity deficit this winter could reach as much as 6GW, around a third of anticipated peak demand. The power shortfall this summer was 2.5GW when Kyiv was already enduring long blackouts.
“It’s time for everybody to understand that this winter could be consequential in Ukraine,” Fatih Birol, director-general of the IEA, told the FT. “It is the most pressing energy security issue today in the world.”
A lack of energy supplies meant a knock-on impact on the operation of hospitals, schools, water supplies and other “major implications”, Birol added.
European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen will meet Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy in Kyiv today to discuss the situation. They will also talk about where to direct €100mn the EU has given Ukraine for repairs and renewable energy, which came from the profits from immobilised Russian assets in the EU.
The EU will also provide €60mn in humanitarian aid for shelters and heaters. Average winter temperatures in Ukraine vary between -4.8C and 2C, according to World Bank figures.
Birol said there were “major shortages” of many crucial parts, including transformers, grid equipment and diesel generators. He said Europe had been too “conservative” in sending electricity to Ukraine and could step up exports without jeopardising European supply.
European consumers could help by cutting their own electricity demand, allowing more power to go to their eastern neighbour. This would be a “very decent way of showing solidarity”, Birol said.
Ukraine should have enough gas to see it through early winter, but the IEA said that once current contracts expire at the end of the year, there could be a need to increase west-to-east gas flows to Ukraine from central and eastern European neighbours.
Chart du jour: Rising tide
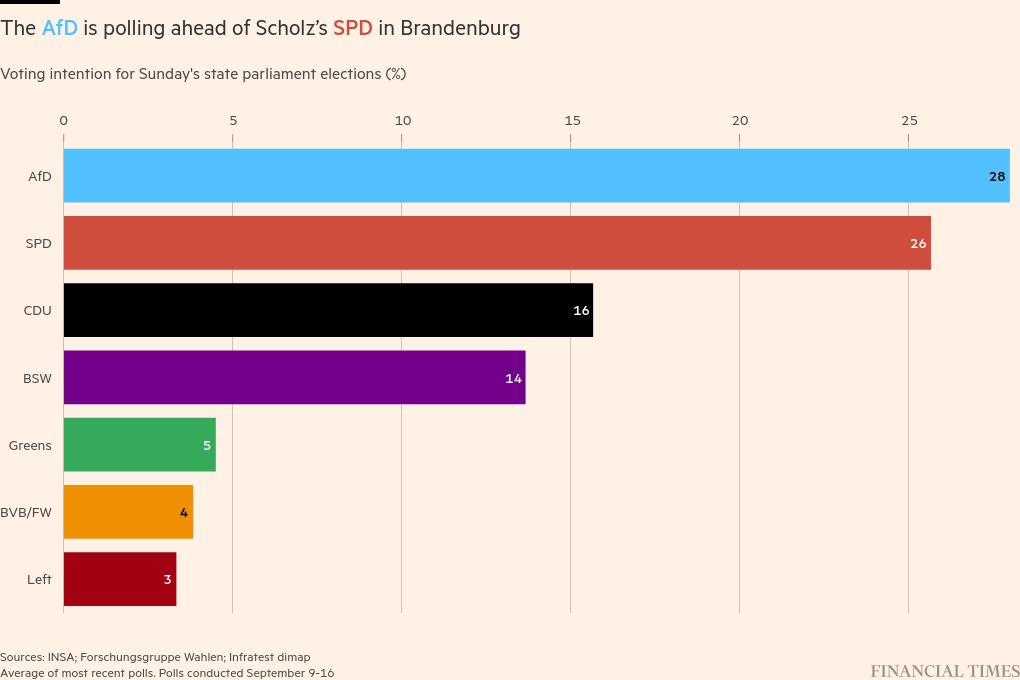
The Alternative for Germany looks set to win another state election in Brandenburg on Sunday, just weeks after the far-right party won its first regional poll in Germany’s postwar history. But the Social Democrats are closing in.
Cut it
If Europe wants to be globally competitive, it needs to go further than what Brussels plans to boost the single market, says a paper co-authored by 20 member states, including the Netherlands and Germany, writes Javier Espinoza.
Context: Two recent landmark reports — by former Italian leaders Mario Draghi and Enrico Letta — spelt out the stark risks of failing to reform the single market. They highlighted the need to reduce regulatory pressure on companies and to make it easier for businesses to access funding in order for the bloc to compete with the US and China.
Ursula von der Leyen’s second term at the head of the European Commission had to “continue to cut red tape . . . going beyond the announced 25 per cent reduction of reporting requirements”, the joint document states, referring to an existing promise.
She should also back “specific digital tools” that would allow companies to focus less on regulatory reporting.
The signatories, which also include Luxembourg and the Czech Republic, called on the commission to provide “an enabling and transparent regulatory environment” — technical language for forcing capitals to align their rules.
Lex Delles, Luxembourg’s economy minister, pointed to persistent barriers within the single market where “retailers cannot pick their suppliers in the country of their choice because of territorial supply constraints imposed by wholesalers”.
He added: “By prohibiting such practices, we would show businesses and consumers that the EU can deliver concrete results for them.”
What to watch today
-
European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen travels to Kyiv.
Now read these
Recommended newsletters for you
Trade Secrets — A must-read on the changing face of international trade and globalisation. Sign up here
Swamp Notes — Expert insight on the intersection of money and power in US politics. Sign up here
Are you enjoying Europe Express? Sign up here to have it delivered straight to your inbox every workday at 7am CET and on Saturdays at noon CET. Do tell us what you think, we love to hear from you: [email protected]. Keep up with the latest European stories @FT Europe